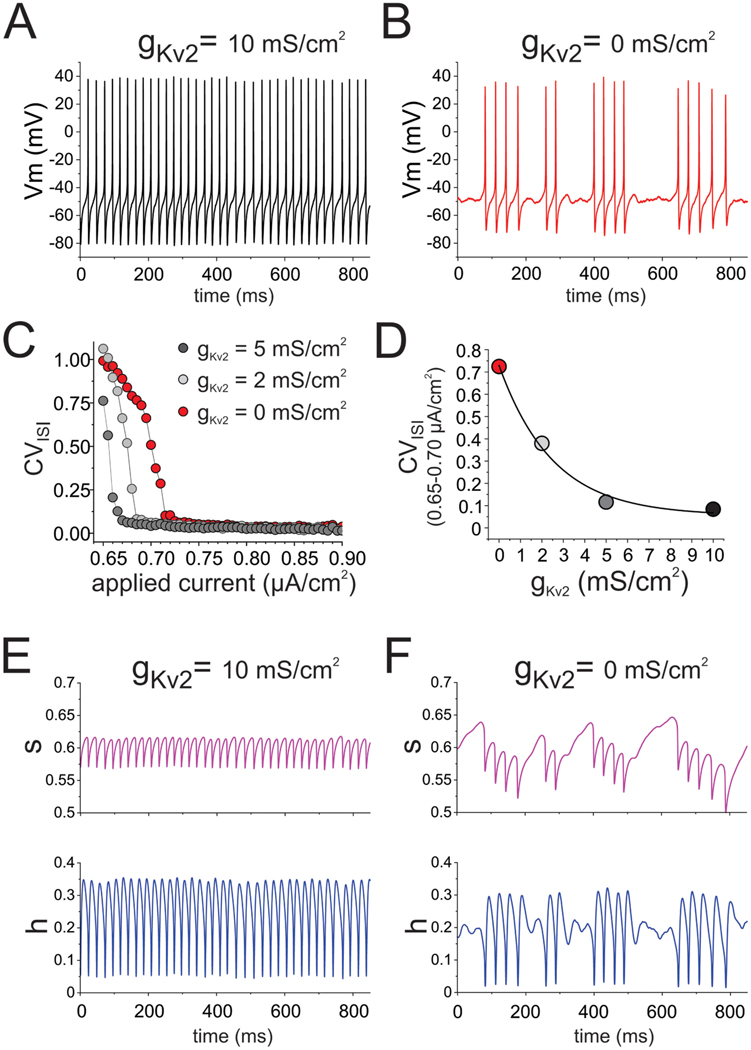
Fig. 3.
Simulations in a fast spiking (FS) cell model assessing the effect of reduced Kv2.1 conductance on the FS cell properties. A) Spike train evoked in the model FS cell with Kv2.1 conductance (gKv2) intact. B) Spike train evoked in the model FS cell without gKv2. C) Plots of the coefficient of variation of the inter spike interval (CVISI) in spike trains as a function of applied current for the model FS cell with intact and reduced levels of gKv2. D) Graph of CVISI in spike trains evoked by applied currents (averaged for 0.65–0.70 μA/cm2) in the model cell with intact and reduced levels of gKv2. E) Time course of the Hodgkin-Huxley inactivation gating variables s (top) and h (bottom) for the FS cell model with intact Kv2, during the spike train shown in A). F) Time course of the Hodgkin-Huxley inactivation gating variables s (top) and h (bottom) for the FS cell model with reduced Kv2, during the spike train shown in B).