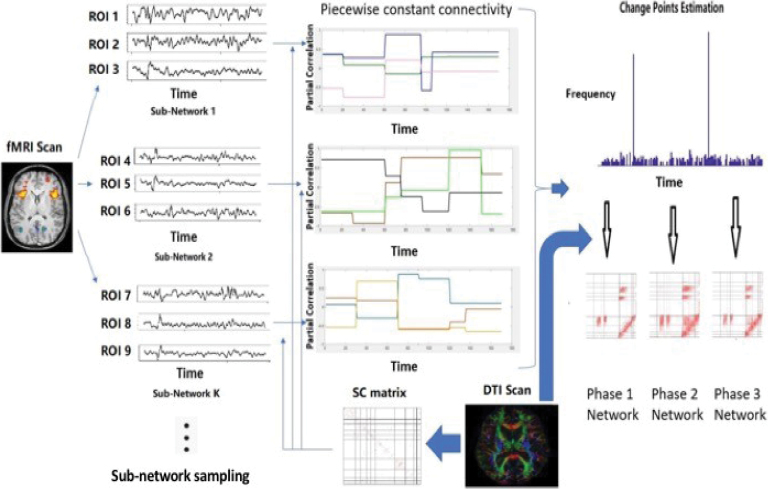
FIG. 1.
A diagrammatic illustration of our novel mDFC approach using Rs-fMRI data, which is guided by brain SC information computed from DTI data. Given a set of nodes in the network, the approach is able to learn change points or jumps in the network in an unsupervised manner, where the number and locations of the change points are unknown and the network is assumed to remain constant within a state phase defined as the time interval between two consecutive change points. The greedy partitioning scheme used to compute change points uses state phase-specific networks that are computed after incorporating brain SC knowledge—in this manner, the change point estimation procedure is influenced by the given brain SC information. To scale up the mDFC approach to high-dimensional networks, we propose a subnetwork sampling scheme where we use the mDFC approach to compute change points using several smaller subsets of nodes or subnetworks. This process is applied repeatedly for a large number of subnetworks, and the set of change points for each subnetwork is recorded. The subnetwork sampling scheme yields a frequency or score for each time point to be identified as a network-level change point, and a systematic data-adaptive thresholding strategy to determine frequency cutoffs that can be used to determine network-level change points that are consistently identified across most subnetworks. Conditional on the estimated network-level change points, the structurally informed precision matrix estimation is applied once again to compute a distinct sparse inverse covariance matrix encoding the network separately for each state phase. The state phase-specific networks are computed by integrating brain SC information that encourages greater weights for FC corresponding to those edges with strong SC under a Gaussian graphical model. DTI, diffusion tensor imaging; FC, functional connectivity; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging; mDFC, multimodal dynamic FC; Rs-fMRI, resting-state fMRI; SC, structural connectivity. Color images are available online.