Figure 3.
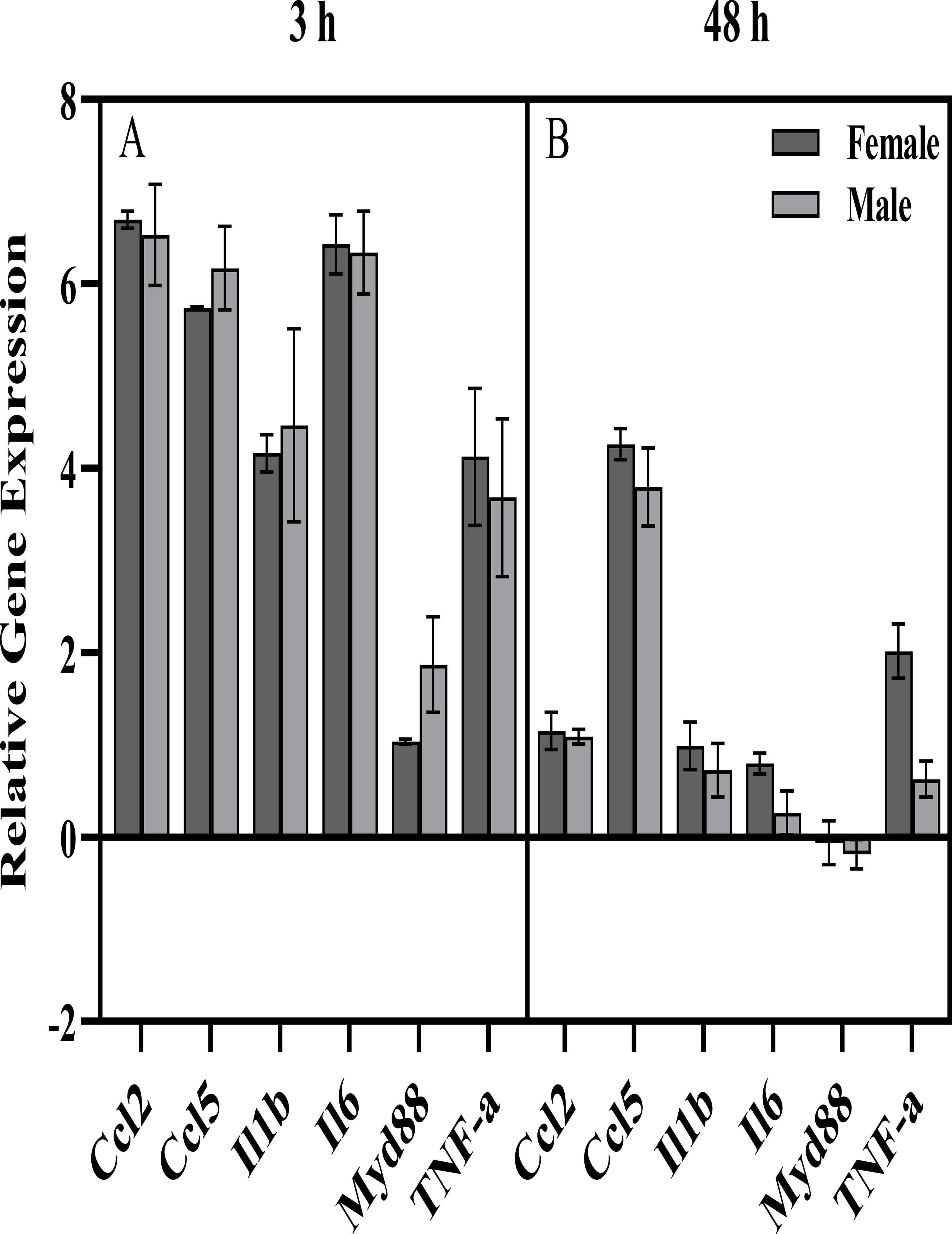
Expression of immune genes in frontal cortex of Camk2a-Sun1 F1 mice A) 3 h and B) 48 h after an injection of Poly(I:C) [PIC] following every other day alcohol consumption. These mice are created by crossing the Camk2a-Cre (https://www.jax.org/strain/005359) and CAG-LSL-Sun1-sfGFP-Myc (https://www.jax.org/strain/021039) mouse lines, which have been used to study cell type-specific responses to perturbations (79). A modification of a previously published behavioral procedure was used (76). Briefly, male and female mice (n=4–7 per group, 8–11 weeks old at the start of the experiment) were injected i.p. with either saline or PIC (10 mg/kg) every 4 days for a total of 13 injections. Ethanol (15% v/v) was available every other day in a two-bottle choice procedure (with water), starting 24 hours after the first PIC injection. Mice were euthanized and frontal cortex was dissected for molecular analysis 3 h or 48 h after the last PIC injection. Expression of 6 genes including 4 pro-inflammatory cytokines, Il6 and Myd88 was measured using qRT-PCR (TaqMan®). Gene Expression was normalized to the saline control of each sex and geometric mean of GusB and 18s (-ddCt, Log2 scale). Error bars represent SEM. Sex x Time ANOVAs revealed significant effects of Time for all genes, with generally lower expression at the 48 h time point, compared to 3 h, but no significant effects of Sex or Sex x Time interactions. One-tailed t-tests comparing PIC group to saline baseline found a significant increase for all genes (except Myd88) of both sexes at the 3 h time point, as well as a significant increase for 4 out of 6 genes for females (Ccl2, Ccl5, Il1b, Il6, TNF-a), and a significant increase for 1 out of 6 genes for males (Ccl5) at the 48 h time point (all p<0.05 Bonferroni-corrected for multiple comparisons).
