Figure 4.
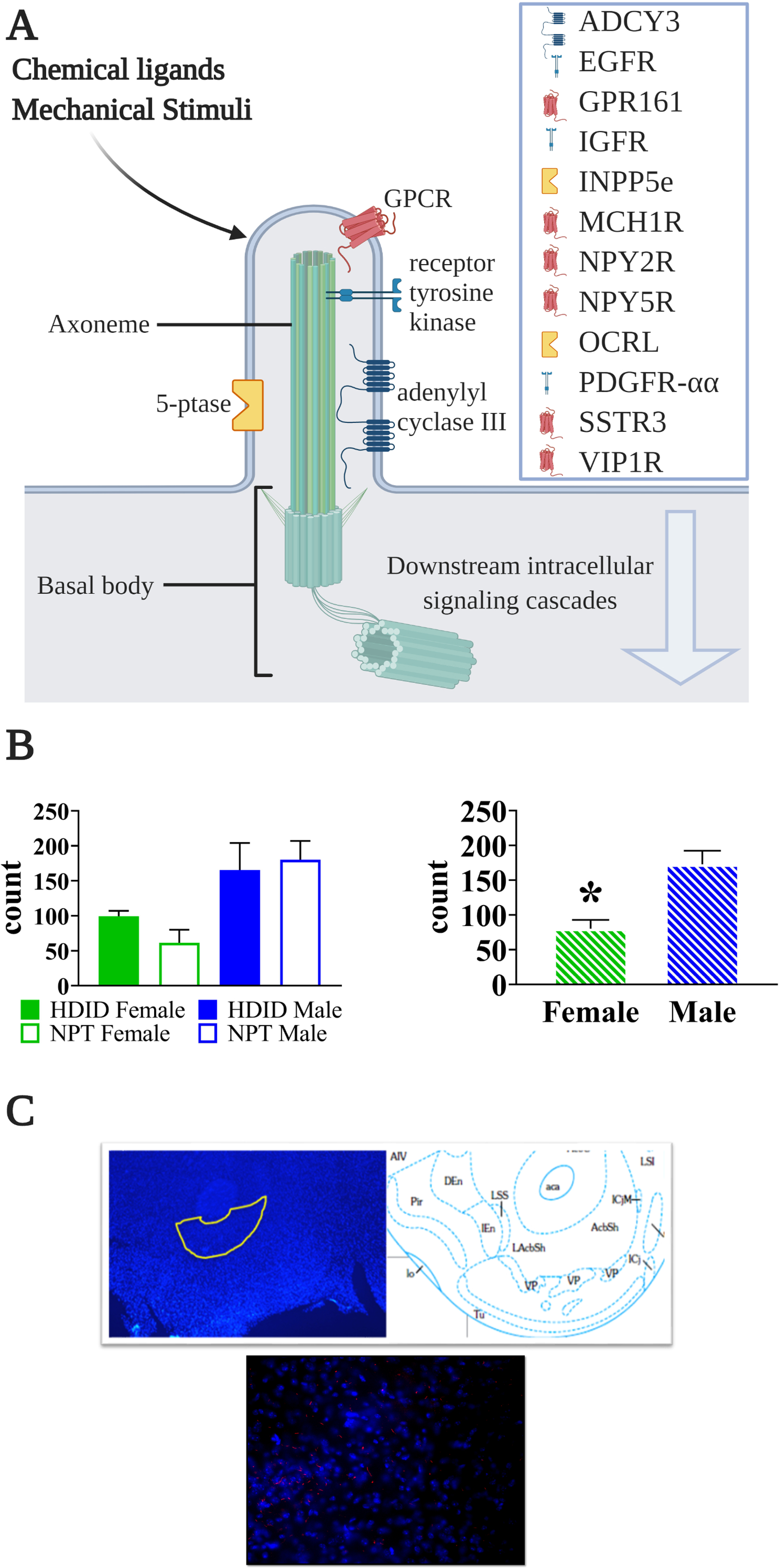
Primary cilia-specific protein (ADCY3) is expressed in greater quantity in the nucleus accumbens core in male than female mice. A) Schematic showing the protrusion of the cell membrane containing the primary cilium. Each cilium core is formed by an axoneme cytoskeletal structure and the cilium is enriched in the listed proteins, some of which are unique to the cilium. The basal body is the cellular organelle from which the cilia extends. Downstream intracellular signaling cascades include Ca2+, Wnt, phosphatidylinositols, and hedgehog, among others. Figure created with Biorender.com. B) Quantification of ADCY3 immunopositive cells counted from the nucleus accumbens core in high drinking in the dark (HDID) selected line mice and their NPT controls (n=3/sex/strain). Although the HDID mice did not differ from the control, male mice did show significantly higher ADCY3 immunoreactivity than female mice (p<0.005). C) Example of ADCY3 immunopositive cells in a nucleus accumbens section from a male mouse. 5-ptase, phosphoinositide 5-phosphatase; ADCY3, adenylate cyclase 3; EGFR, epithelial growth factor receptor; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor; GPR161, G protein-coupled receptor161; IGFR, insulin-like growth factor receptor; INPP5e, inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase; MCH1R, melanin-concentrating hormone 1 receptor; NPY2R, neuropeptide Y2 receptor; NPY5R, neuropeptide Y5 receptor; OCRL, oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe; PDGFR-αα, platelet-derived growth factor receptor α homodimer; SSTR3, somatostatin receptor isoform 3; VIP1R, vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor
