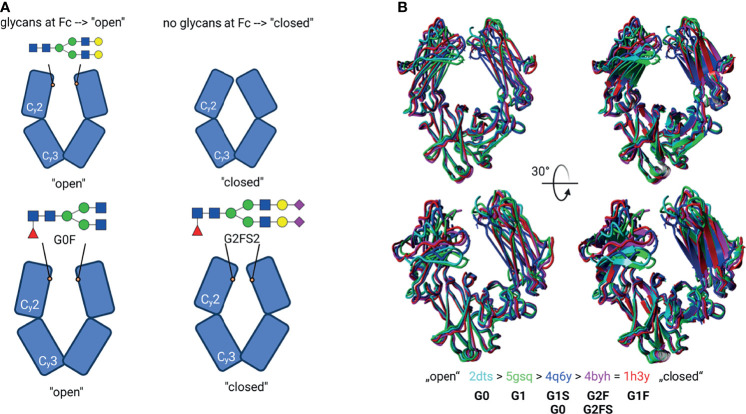
Figure 4.
Glycosylation-induced conformational changes. (A) Schematic model of the IgG Fc structure with or without glycans. Top: Glycan structures by self-induce conformational changes, resulting in an “open” structure. The de-glycosylated Fc have a “closed” structure instead. Bottom: Suggested model for individual glycan-induced conformational changes. Different glycan structures are discussed to influence the distance between the Cγ2 domains. E.g., sialylated (G2FS2) glycans lead to a sterically closer conformation of Cγ2 to each other. Created with BioRender.com (B) Superpose of different Fc structures. The PDB entries correspond to the colour code in the cartoon- and tube-styled structures; additionally, their glycan structures are given. The structures were classified as “open” and “closed” conformation. The structures were superimposed using YASARA. The N-glycans were created using GlycoWorkbench 2.1 (4).