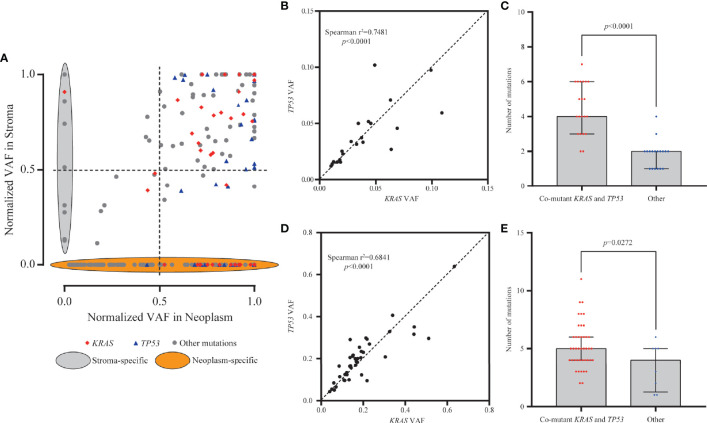
Figure 3.
Clonality and mutation burden analysis of KRAS in stromal and neoplastic components. (A) Variant allele frequencies (VAFs) of each mutation were normalized with maximum VAF in the same specimen to assess the clonality. Mutations with ≥50% normalized VAFs were more likely to be clonal events; 86.8% of common mutations were clonal events in stroma. (B, D) The VAFs of KRAS and TP53 mutations showed statistically significant consistency in the stromal (Spearman’s r2 = 0.7481, p < 0.0001) and neoplastic (Spearman’s r2 = 0.6841, p < 0.0001) components, indicating that mutants KRAS and TP53 might have co-occurred around the same early period. (C, E) Samples with co-mutants KRAS and TP53 tended to harbor more mutations than the other mutant subtype samples, in both stromal (p < 0.0001) and neoplastic (p = 0.0272) components.