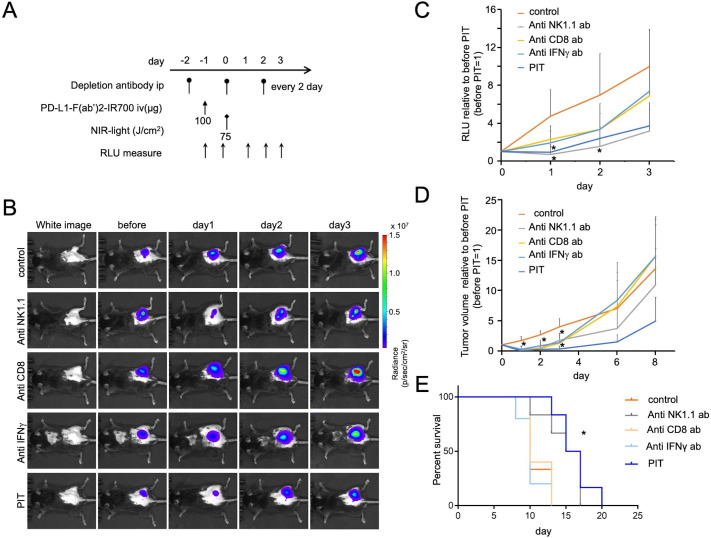
Figure 5.
PD-L1-targeted NIR-PIT induces antitumor effects via partially on CD8 T and NK cells and IFN-γ production. (A) PD-L1-targeted NIR-PIT regimen involving PD-L1-F(ab′)2-IR700 injection, intraperitoneal injection of neutralized antibodies, and NIR-light exposure is shown. Depletion antibodies were injected every 2 days. (B) Representative in vivo BLI of tumor-bearing mice (right flank tumor). (C) Quantitative RLU showed a significant decrease in PD-L1-targeted NIR-PIT-treated tumors but was inhibited by adding the depletion or neutralization antibodies (n=5–6 in each group) (control group vs PIT and anti NK1.1 group at day 1: *p<0.01; control group vs anti NK1.1 group at day 2: *p<0.05, Tukey’s test with ANOVA). (D) Tumor volume ratio (before NIR-PIT=1) is demonstrated. NIR-PIT introduced on day 0 led to significant reductions in the tumor volume ratio but inhibited with adding the depletion or neutralization antibodies (n=5–6 in each group) (control group vs all other groups at day 1: *p<0.0001; control group vs anti CD8 and anti NK1.1 groups at day 2: *p<0.001; control group vs anti IFN-γ group at day 2: *p<0.01; control group vs PIT group at day 2: *p<0.0001; control group vs anti-CD8 group at day 3: *p<0.05; control group vs anti-NK1.1 and anti IFN-γ groups at day 3: *p<0.01; control group vs PIT group at day 3: *p<0.001, Tukey’s test with ANOVA). (E) The survival of PD-L1-targeted NIR-PIT was shortened by adding the depletion or neutralization antibodies (n=5–6 in each group) (*p=<0.001 (0.0007), log-rank test). ANOVA, analysis of variance; BLI, bioluminescence imaging; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; NK, natural killer; NIR-PIT, near-infrared photoimmunotherapy; PD-L1, protein programmed death-ligand 1; RLU, relative light unit.