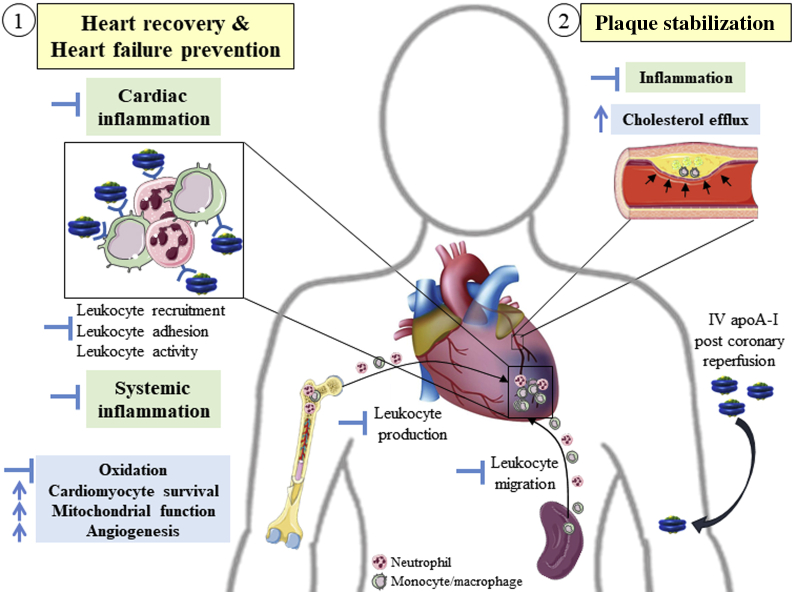
Figure 1.
Potential Pleiotropic Effects of ApoA-I Mediating Cardiac Protection Post–Myocardial Infarction
When delivered immediately following myocardial infarction, apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) may (1) improve cardiac recovery and preserve cardiac function via inhibition of excessive cardiac and systemic inflammation, as well as via immunoindependent cardioprotective effects; and (2) reduce the risk for recurrent events by stabilizing atherosclerotic plaque by increasing cholesterol efflux and limiting plaque inflammation. Green, anti-inflammatory mechanisms; blue, other mechanisms.