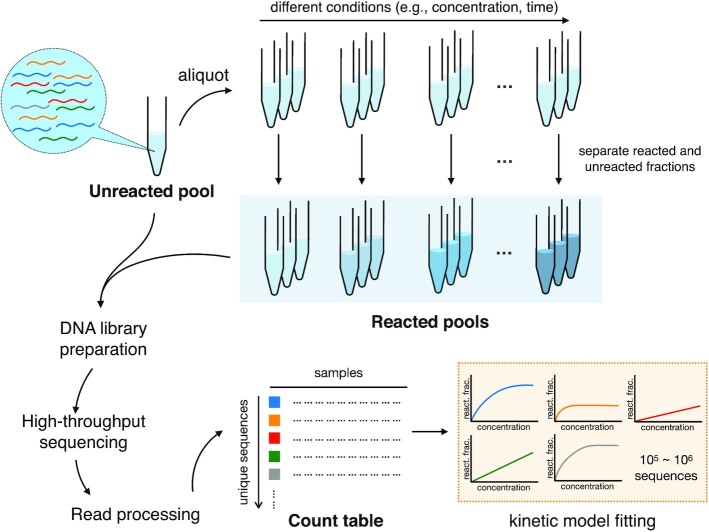
Figure 1.
General scheme of k-Seq experiment and analysis. A heterogeneous input pool containing nucleic acids is reacted at different experimental conditions (e.g. different substrate concentrations or different reaction time). Reacted and unreacted molecules are separated and either (or both) of these fractions is prepared for high-throughput sequencing. The reads from DNA sequencing are processed to obtain a count table for each unique sequence across samples, normalized by a standard, and abundances across samples are fit into a kinetic model to estimate parameters (e.g. rate constants). react. frac. = reacted fraction.