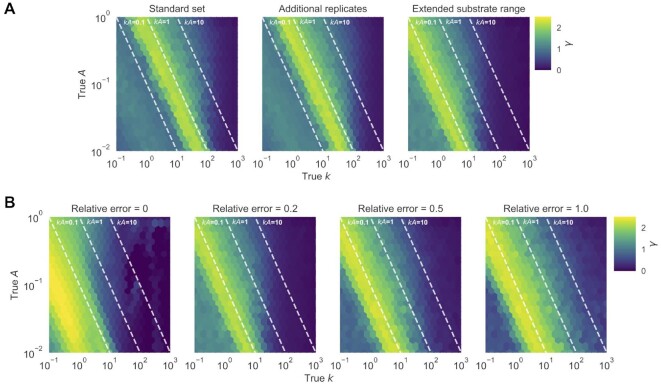
Figure 2.
Effect of experimental factors on model identifiability to separately estimate
 and
and  .
Identifiability was evaluated using metric
.
Identifiability was evaluated using metric 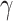 , based on the
simulated effects of (A) choice of BYO samples (with relative error =
0.2) and (B) relative error (using the BYO series of the extended
substrate range). Reacted fractions for 10 201 (1012) simulated sequences
with true
, based on the
simulated effects of (A) choice of BYO samples (with relative error =
0.2) and (B) relative error (using the BYO series of the extended
substrate range). Reacted fractions for 10 201 (1012) simulated sequences
with true 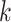 ,
, 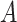 in the parameter
space shown in the figure were fit to the pseudo-first order model, and
in the parameter
space shown in the figure were fit to the pseudo-first order model, and
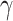 values for each sequence were
calculated from 100 bootstrapped samples. Higher values of
values for each sequence were
calculated from 100 bootstrapped samples. Higher values of 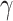 indicate that
indicate that 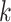 and
and 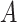 are less
separable. (A) Choosing a wider range of BYO concentration is more effective in
improving the region of identifiable data compared to adding more replicates of the
same BYO concentrations. (B) With higher measurement error,
are less
separable. (A) Choosing a wider range of BYO concentration is more effective in
improving the region of identifiable data compared to adding more replicates of the
same BYO concentrations. (B) With higher measurement error, 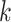 and
and
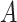 become increasingly difficult to
estimate separately.
become increasingly difficult to
estimate separately.