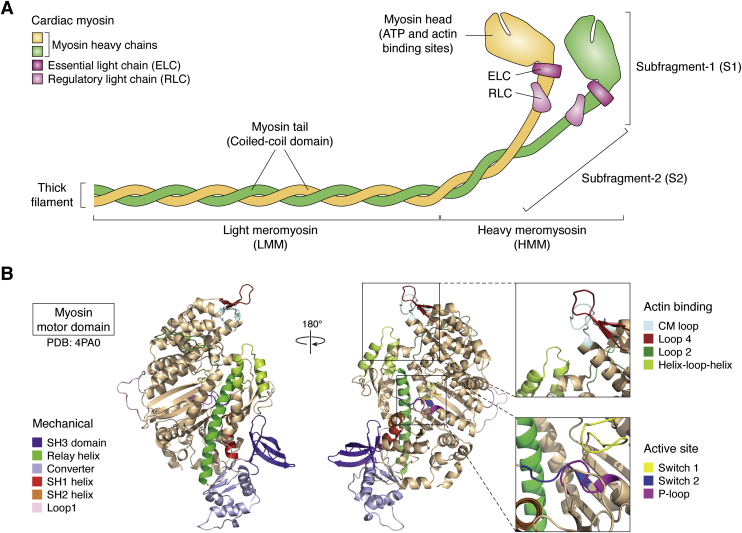
Figure 1.
Cardiac myosin structure.A, schematic structure of cardiac myosin showing the regions named for proteolytic fragments heavy meromyosin (HMM), light meromyosin (LMM), subfragment-1 (S1), and subfragment-2 (S2). Full-length myosin consists of two heavy chains (yellow and green), each bound to an essential light chain (ELC, dark pink) and a regulatory light chain (RLC, light pink). The myosin heads (S1 region) contain the sites of ATP and actin binding. The tails (LMM) are coiled coils that assemble into the thick filament. B, structure of the human cardiac myosin motor domain based on PDB ID 4PA0, where the loops not resolved in the crystal structure were modeled using homology modeling. Structural domains related to the mechanical power stroke, actin binding, and nucleotide binding to the active site are highlighted. For additional details on the structural mechanism of myosin force generation, the reader is referred to (7).