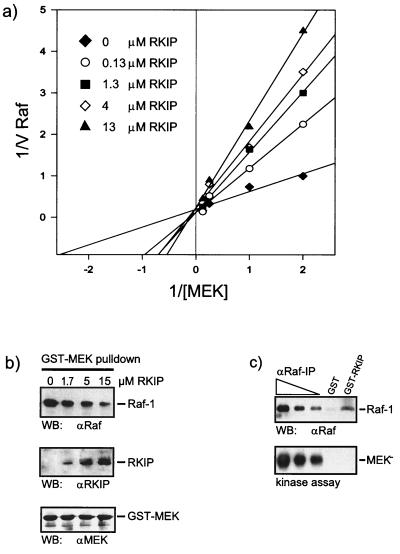
FIG. 3.
RKIP inhibits Raf-1 by a competitive mechanism. (a) Lineweaver-Burk plot of Raf-1 inhibition by RKIP. Activated GST–Raf-1 was used to phosphorylate GST–MEK-1 in the presence of increasing amounts of RKIP, as indicated. Phosphorylation was quantified with a Fuji phosphorimager. The data shown are the averages of three independent experiments. (b) RKIP disrupts the Raf-1–MEK complex. GST-MEK and Raf-1 were coexpressed in Sf-9 cells. The GST-MEK–Raf-1 complex was purified by adsorption to glutathione Sepharose beads, washed, and resuspended in PBS. Purified RKIP was added at the concentrations indicated. After 1 h at 4°C, the GST-MEK beads were washed three times with PBS and examined for associated proteins by Western blotting (WB) with the indicated antisera. (c) Raf-1 bound to RKIP does not phosphorylate MEK. A lysate of Sf-9 cells expressing activated Raf-1 was incubated with 5 μg of GST or GST-RKIP beads. Serial dilutions of the same lysate were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Raf serum crafVI. After three washes with PBS, the pellets were resuspended in kinase buffer and incubated with 100 μM ATP and kinase-negative MEK as substrate. MEK phosphorylation was visualized by immunoblotting with a phospho-MEK-specific antiserum. Raf-1 was stained with crafVI.