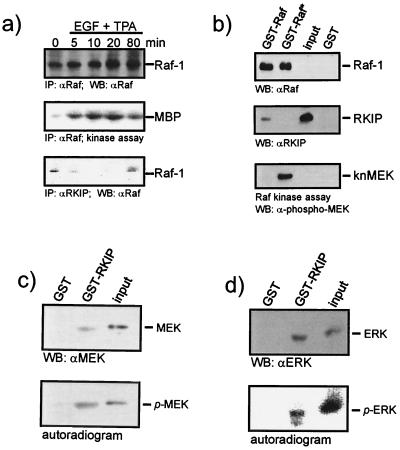
FIG. 4.
Analysis of RKIP binding to activated Raf-1, MEK, and ERK. (a) Mitogen activation of Raf-1 decreases its association with RKIP. COS-1 cells were transiently transfected with Raf-1 and RKIP expression vectors. Serum-starved cells were treated with epidermal growth factor (EGF) (20 ng/ml) plus TPA (100 ng/ml) for the times indicated. Raf-1 immunoprecipitates were analyzed for kinase activity, and RKIP immunoprecipitates were examined for Raf-1. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot. (b) Purified RKIP produced in E. coli was tested for binding to GST-Raf and activated (*) GST-Raf beads. GST-Raf proteins were produced in Sf-9 cells and activated by coexpression of RasV12 and Lck. An aliquot of the GST-Raf beads was examined for phosphorylation of kinase-negative MEK (knMEK). (c and d) MEK and ERK proteins were phosphorylated in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP and tested for binding to GST-RKIP beads. Binding of phosphorylated proteins was detected by autoradiography. Binding of total protein was visualized by Western blotting (WB). The contribution of phosphoproteins to the Western blot signal is minimal, because they represent less than 10% of the total protein.