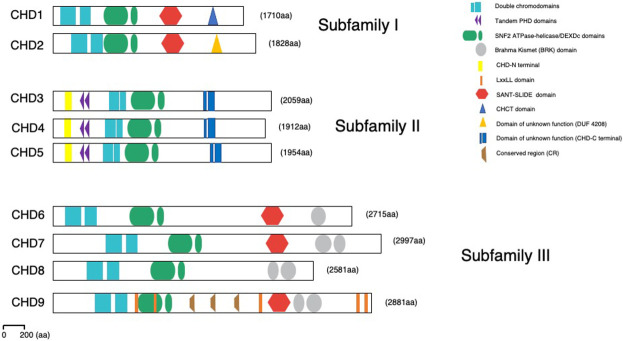
Figure 1.
Structural domain organization of the CHD enzymes. Domain representation of all three CHD subfamilies as indicated in the text. All CHDs have double chromodomains (blue squares) and SNF2-like ATPase/DEXDc helicase domains (green ovals). Subfamily II members contain tandem PHD Zn finger-like domains (purple triangles). Subfamily III members have additional Brahma Kismet (BRK) domains at the C terminus (gray oval); enzymes of both subfamilies I and III contain SANT-SLIDE domains at C terminus (red hexagon). These domains facilitate engagement and stabilization of the interaction with the chromatin substrate and allow efficient ATP hydrolysis and DNA translocation. Recently, a number of novel structural domains have been identified: CHD-N-terminal, CHD-C-terminal, CHCT, DUF4208, and conserved region (CR). CHD9 associates with nuclear receptors through LxxLL recognition motifs (orange stripes).