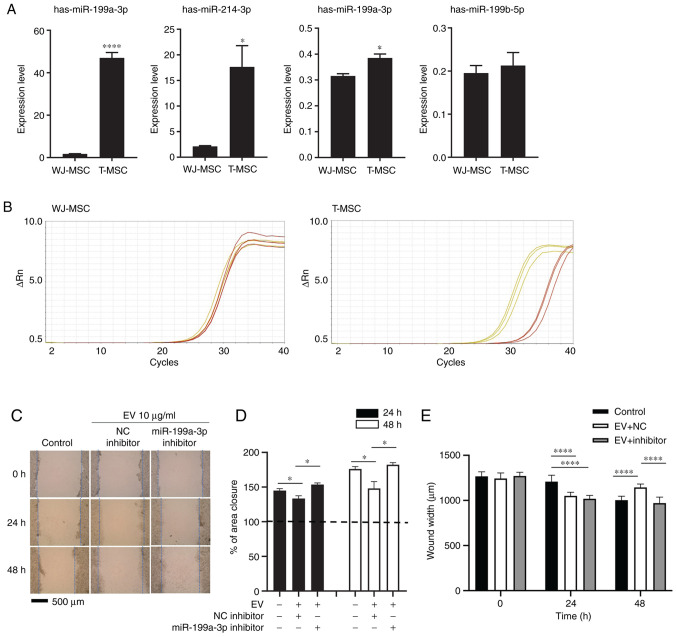
Figure 3.
miR-199a-3p inhibitor attenuates the effect of T-MSC EVs on scratch wound healing assay. (A) EV RNA from WJ-MSCs and T-MSCs was extracted at 80% confluence and analyzed by reverse transcription-qquantitative PCR. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM and analyzed by Student t-test *P<0.05, ****P<0.0001. (B) Amplification plot. Yellow, hsa-miR-199a-3p; red, control (RNU6-1). (C) Migration of HepG2 cells following transfection and addition of EVs with NC or miR-199a-3p inhibitor. Magnification, ×40. (D) Closure area was calculated after 24 or 48 h. A total of >10 fields of view were analyzed and each experiment was repeated three times. Statistical significance was determined by t test. (E) Wound width was measured and distance was calculated (n=10 per field). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with multiple comparison by Sidak test *P<0.05, ****P<0.0001 vs. WJ-MSC. Untreated, miRNA NC- and miR-199a-3p inhibitor-treated HepG2 cells were used as the control, NC and inhibitor, respectively. miR, microRNA; T-MSC, tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cell; EV, extracellular vesicle; WJ, Wharton's jelly; NC, negative control.