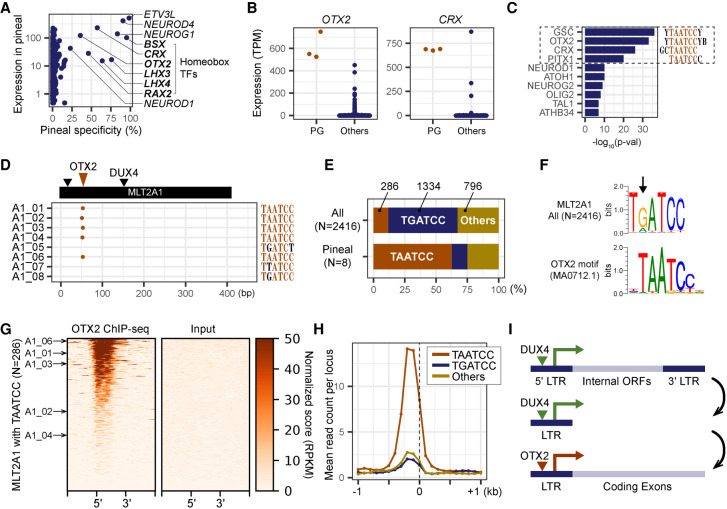
Figure 6.
OTX2 as a potential regulator of MLT2A elements in pineal gland. (A) Scatter plot of the levels of pineal gland expression of 1665 human transcription factors. The x-axis indicates the specificity of pineal gland expression (pineal gland expression as a percentage of the total expression of all samples). Gene names of the top 10 transcription factors (displaying the highest pineal specificity) are listed. (B) Normalized expression values of OTX2 and CRX genes in three pineal glands (PG) and 715 other samples. (C) The top 10 transcription factors significantly enriched in promoter regions of pineal-specific genes identified by using HOMER. (D) Distribution of OTX2 binding motifs (MA0712.1) in eight MLT2A1 elements; the motifs were identified by using MAST software. (E) The percentages of MLT2A elements that have TAATCC, TGATCC, or other hexamer sequences. (F) Sequence logos of OTX2 motif-enriched regions in MLT2A1 and the original OTX2 motif. (G) OTX2 binding states in 286 MLT2A elements that have the TAATCC sequence and flanking regions (±1 kb) for ChIP-seq and input samples. The pineal-active five MLT2A elements are denoted by arrows. (H) Normalized ChIP-seq read counts on MLT2A1 elements that have TAATCC (N = 286), TGATCC (N = 1334), or other (N = 796) sequences. (I) Schematic representation of the transition of LTR retrotransposons from full-length to the solo-LTR fused to a protein-coding gene.