Figure 2.
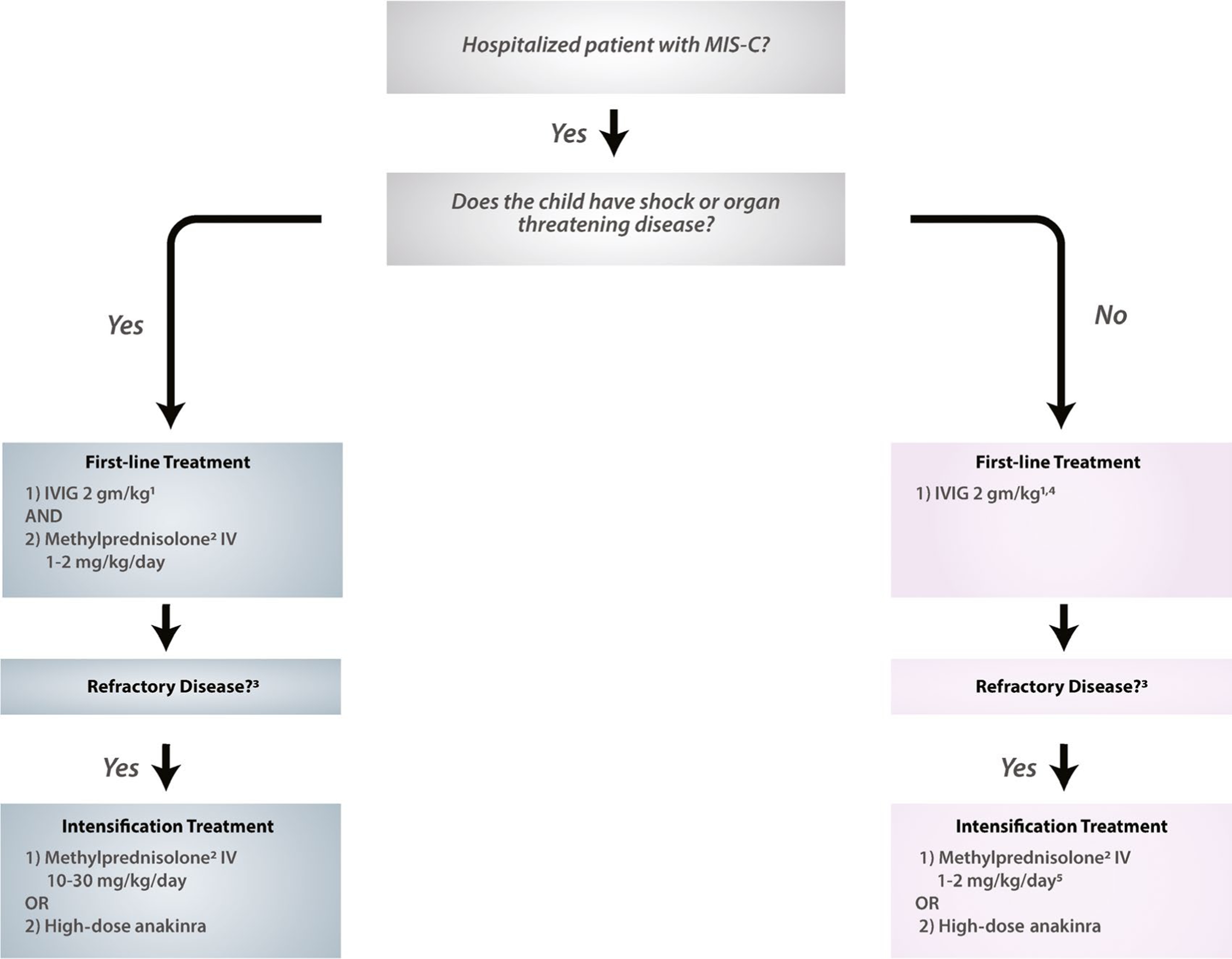
Algorithm for initial immunomodulatory treatment of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Moderate-to-high consensus was reached by the Task Force in the development of this treatment algorithm for MIS-C associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. 1Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) dosing is 2 gm/kg based on ideal body weight. Cardiac function and fluid status should be assessed before IVIG is given. In some patients with cardiac dysfunction, IVIG may be given in divided doses (1 gm/kg daily over 2 days). 2Methylprednisolone or another steroid at equivalent dosing may be used. 3Refractory disease is defined as persistent fevers and/or ongoing and significant end-organ involvement. 4Low-to-moderate–dose glucocorticoids (methylprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg/day) may be considered for first-line therapy in some MIS-C patients with concerning features (ill appearance, highly elevated B-type natriuretic peptide levels, unexplained tachycardia) who have not yet developed shock or organ-threatening disease. 5If the patient was given low-to-moderate–dose glucocorticoids as first-line therapy, methylprednisolone IV dosing should be 10–30 mg/kg/day for intensification treatment.
