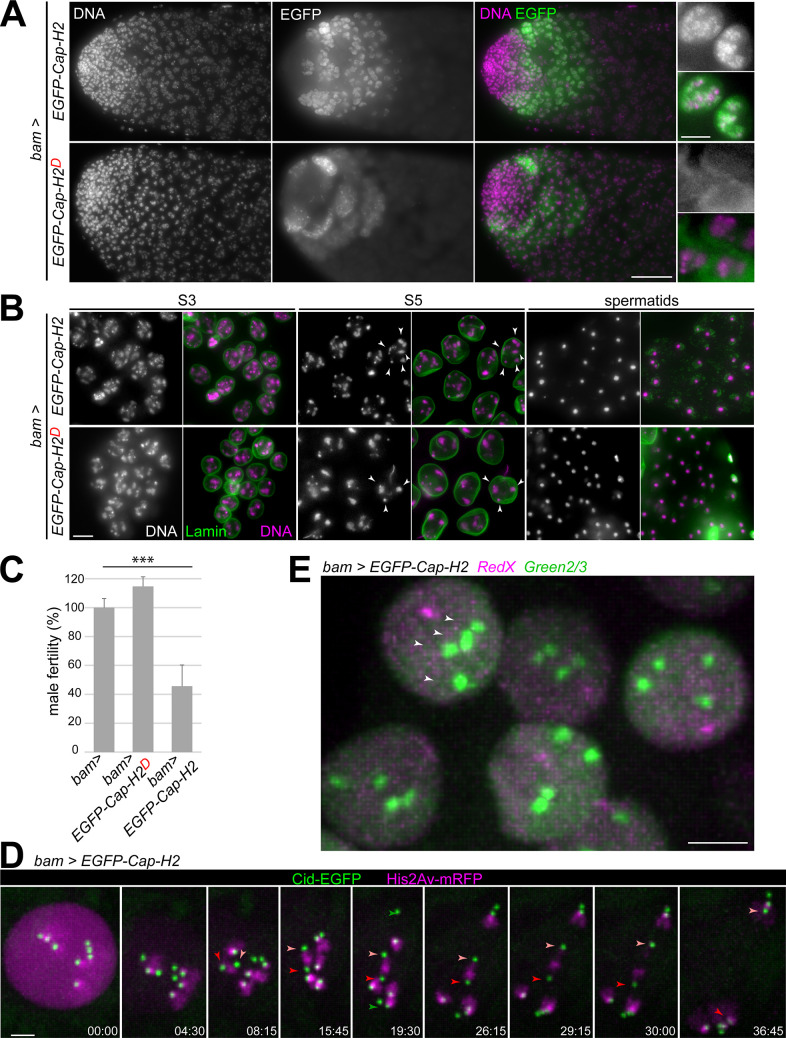
Fig 8. Increased Cap-H2 levels inhibit the pairing of autosomal homologs.
(A-D) UASt-EGFP-Cap-H2 (encoding isoform F) and UASt-EGFP-Cap-H2D (encoding isoform D) were expressed in spermatocytes using bamP-GAL4-VP16. (A) EGFP signals and DNA staining in testis tip regions (left) and high magnification views with S3 spermatocytes (right). EGFP is present only transiently in early spermatocytes on chromatin (EGFP-Cap-H2) and cytoplasm (EGFP-Cap-HD). (B) Expression of UASt-EGFP-Cap-H2 results in too many chromosome territories (arrowheads) and meiotic chromosome missegregation in contrast to UASt-EGFP-Cap-H2D. Spermatocytes at the stages S3 and S5 are displayed, as well as early round spermatids (sp), after labeling testis squash preparations with anti-Lamin Dm0 and a DNA stain. (C) Fertility of males with the indicated genotypes. Four test crosses, each with a single male parent, were set up and the resulting number of F1 progeny was counted. Mean fertility of bam-GAL4-VP16 males without a UAS transgene (bam>) was set to 100%. *** indicates p < .001 (t test) and whiskers s.d. (D) Progression through MI was analyzed by time-lapse imaging of spermatocytes with bam>EGFP-Cap-H2, His2Av-mRFP and Cenp-A/Cid-EGFP. Time (min:sec) is indicated relative to the onset of NEBD I. Arrowheads indicate the centromeres of chr4 (green), chrX (dark red) and chrY (light red). After stable bi-orientation of the sex chromosome bivalent (t = 15:45), chrX and chrY are separated apart regularly during anaphase I (last three still frames). In contrast, autosomes are present as univalents at the start of M I, which segregate randomly after failure of congression into a metaphase plate (as indicated for example by chr4). (E) Live imaging of spermatocytes with bam>EGFP-Cap-H2, RedX and Green2/3. Four Green2/3 dots (arrowheads) are present already in early S1/2 spermatocytes. Scale bars = 40 μm (A, left), 10 μm (A, right), 5 μm (B, D), 3 μm (E).