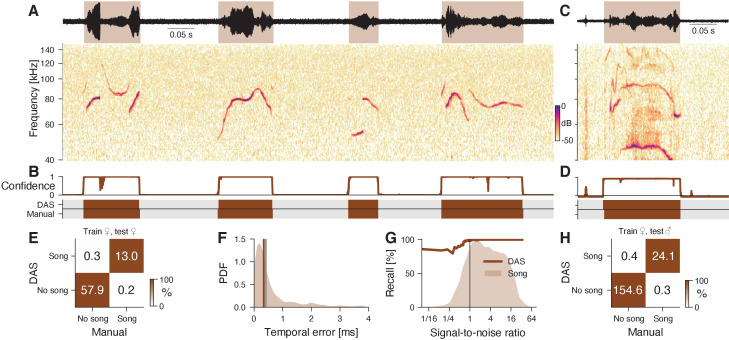
Figure 2. DAS performance for mouse ultrasonic vocalizations.
(A) Waveform (top) and spectrogram (bottom) of USVs produced by a female mouse in response to an anesthetized female intruder. Shaded areas (top) show manual annotations. (B) Confidence scores (top) and DAS and manual annotations (bottom) for the female USVs in A. Brief gaps in confidence are filled smooth annotations. (C) Example of male USVs with sex-specific characteristics produced in the same assay. (D) Confidence scores (top) and DAS and manual annotations (bottom) for the male USVs in C from a DAS network trained to detect female USVs. (E) Confusion matrix from a female-trained network for a test set of female USVs. Color indicates the percentage (see color bar) and text labels the seconds of song in each quadrant. (F) Distribution of temporal errors for syllable on- and offsets in female USVs. The median temporal error is 0.3 ms for DAS (brown line) and 0.4 ms for USVSEG Tachibana et al., 2020, a method developed to annotate mouse USVs (gray line). (G) Recall of the female-trained network (brown line) as a function of SNR. The brown shaded area represents the distribution of SNRs for all samples containing USVs. Recall is high even at low SNR. (H) Confusion matrix of the female-trained DAS network for a test set of male USVs (see C, D for examples). Color indicates the percentage (see color bar) and text labels the seconds of song in each quadrant.