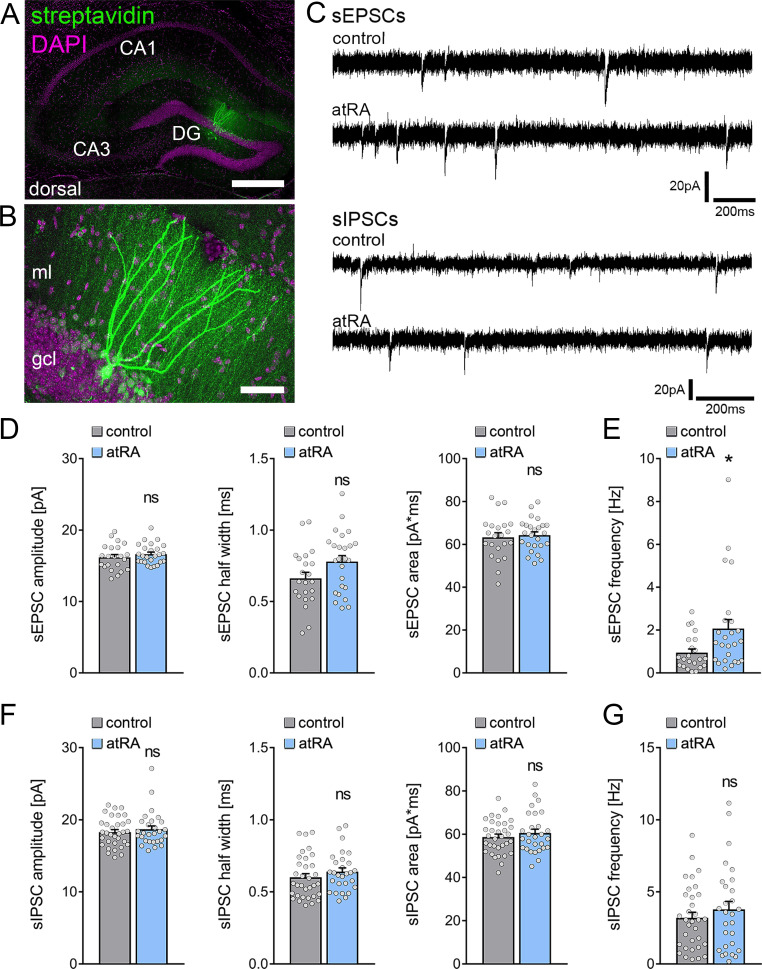
Figure 1. All-trans retinoic acid (atRA) induces no major changes in excitatory and inhibitory synaptic strength in dentate granule cells of the dorsal hippocampus.
(A, B) Example of patched and post hoc identified dentate granule cell in acute slices prepared from the dorsal hippocampus. Scale bar (upper panel)=500 µm; Scale bar (lower panel)=50 µm. (C) Sample traces of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) and spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) recorded from dentate granule cells of atRA (10 mg/kg; i.p.)-treated or vehicle-only (control) animals. (D, E) Group data of sEPSC recordings. A significant increase in the sEPSC frequency is observed (ncontrol=22 cells, natRA=25 cells in four animals; Mann-Whitney test, UsEPSC frequency=175). (F, G) Group data of sIPSC recordings (ncontrol=33 cells, natRA=28 cells in four animals; Mann-Whitney test). Individual data points are indicated by gray dots. Values represent mean ± SEM. (*, p<0.05; ns, non-significant difference). DG, dentate gyrus; gcl, granule cell layer; ml, molecular layer.