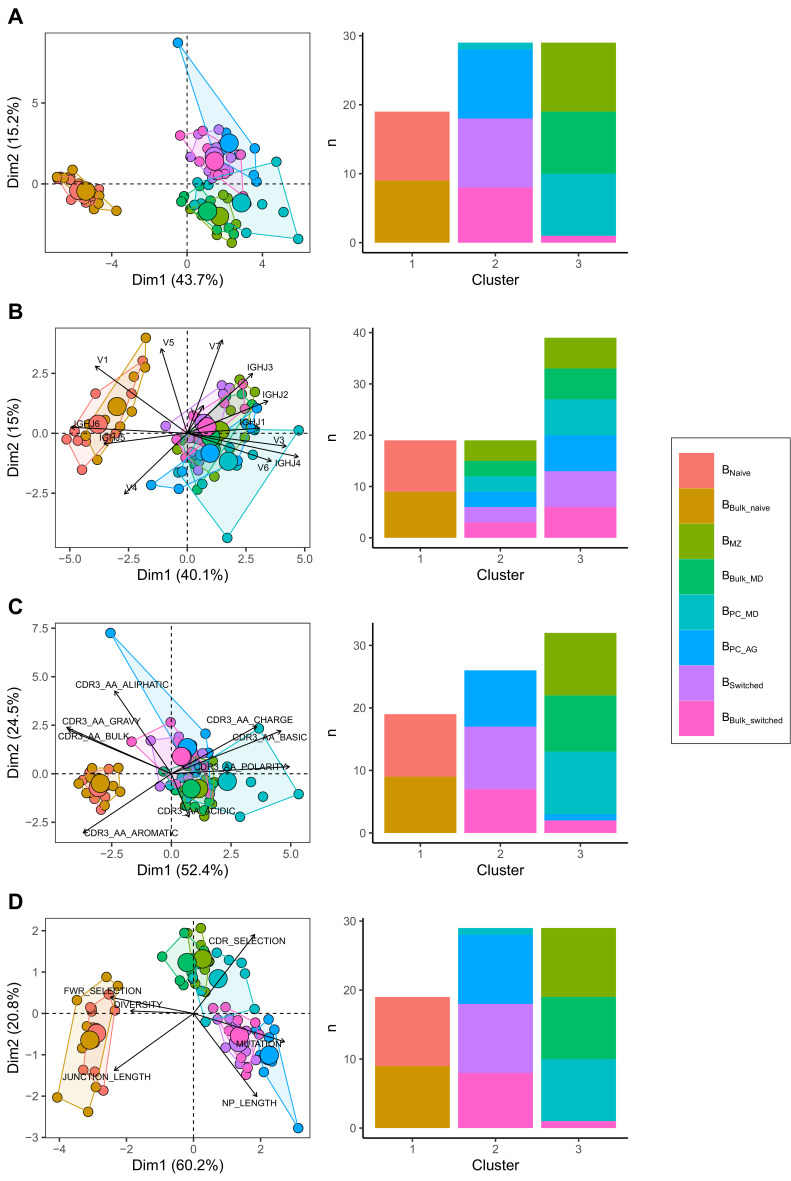
Figure 1. Different repertoire characteristics similarly separate between B cells subpopulations.
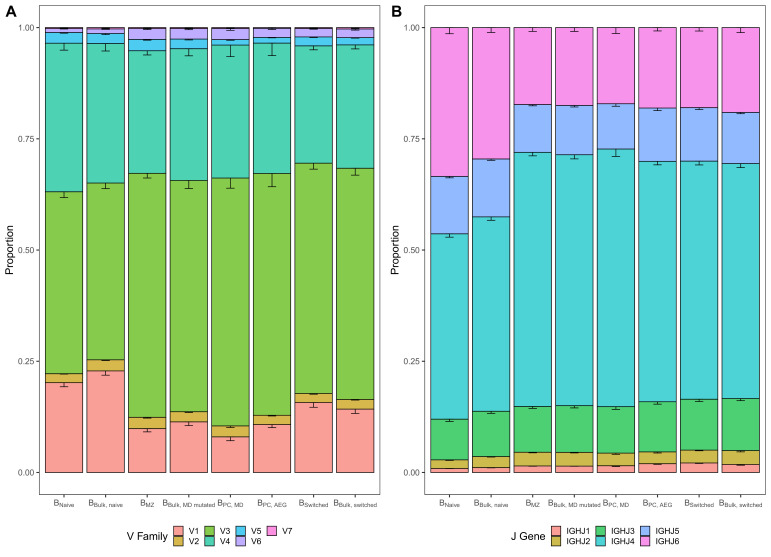
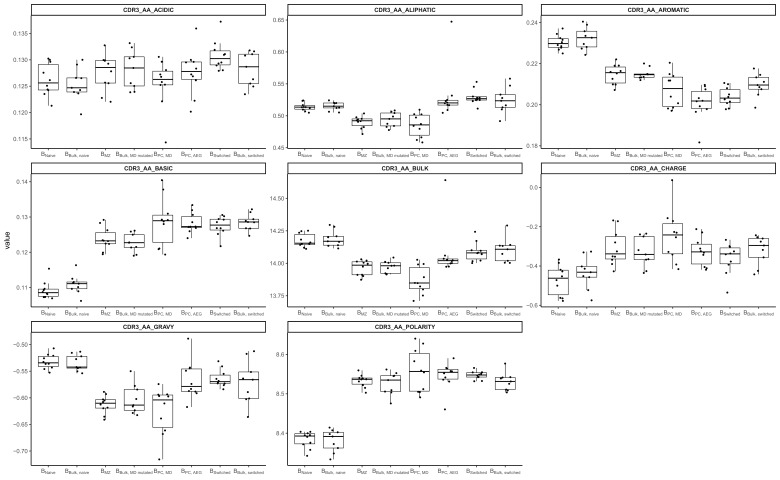
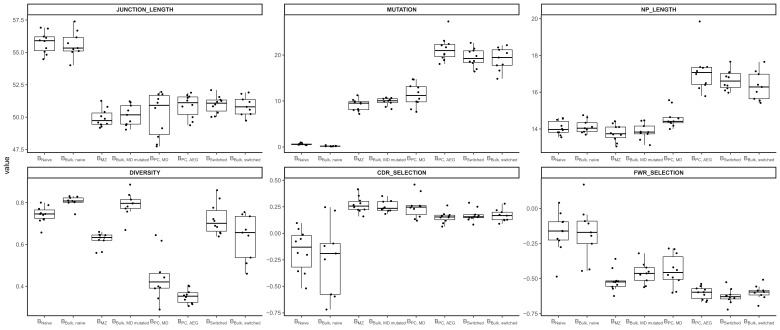
Principal component analysis (PCA) (left) and composition of the clusters formed using k-means clustering with k = 3 (right) applied on (A) all repertoire characteristics, (B) V family and J gene usage (see Figure 1—figure supplement 1), (C) physiochemical properties of CDR3 junction (see Figure 1—figure supplement 2) and (D) global repertoire metrics (see Figure 1—figure supplement 3). The percentage of all variation in the data that is explained by PC1 and PC2 is shown on the x and y axis, respectively, between brackets. In the PCA plots, areas are the convex hulls of the subsets, and the largest point of one colour represents the centre of that hull.