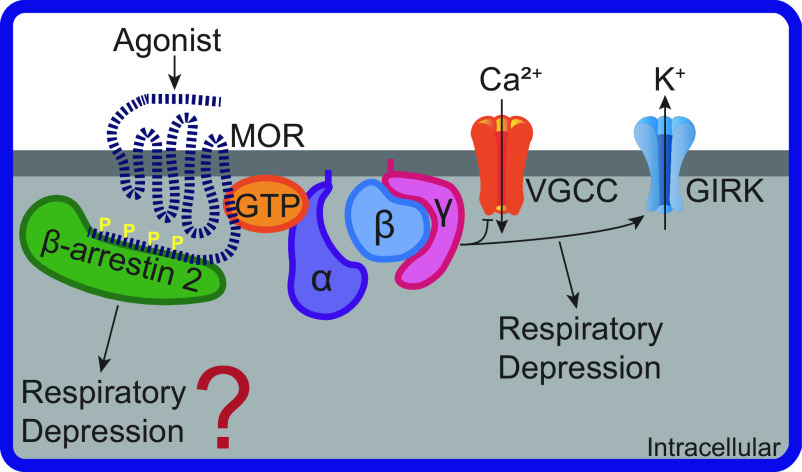
Figure 1.
Mu opioid receptor cellular signaling pathways involved in respiratory depression. Agonist binding to mu-opioid receptor (MOR) activates heterotrimeric G protein subunits: alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ). Gβγ inhibits voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC) and activates G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GIRK). β-arrestin 2 binds to MOR with carboxy-terminal phosphorylation sites (P). GIRK, but likely not β-arrestin 2, activity can lead to respiratory depression.