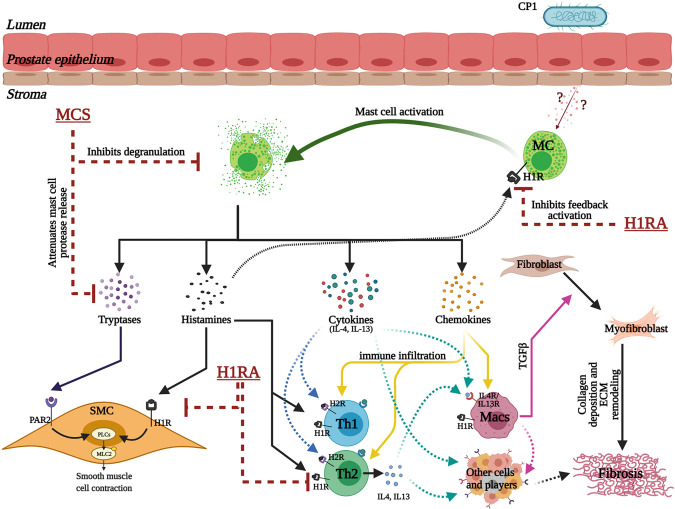
Figure 10.
Schematic illustration of the crucial multifaceted role played by prostate mast cells (MCs) in facilitating prostatic inflammation, fibrosis, and smooth muscle contraction in the development of lower urinary tract symptoms. Intraurethral instillation of CP1 in mice triggers epithelial tissue damage that induces the release of as yet unknown factors that lead to an increase in MC numbers and activation in the mouse prostate stroma. Activated MCs, in turn, release a plethora of factors that include tryptases (and other proteases), histamines, cytokines (including IL-4 and IL-13), and chemokines. Tryptases and histamine released from MCs act on smooth muscle cells (SMCs) via protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) and histamine 1 receptors (H1Rs), respectively, leading to phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated regulation of SMC contraction. Histamine released from activated MCs also triggers a feedback loop to further activate MCs through histamine receptors on MCs. The chemokines released trigger increased immune cell infiltration and proliferation. The cytokines released from MCs lead to activation of T helper (Th)1, Th2, and Th17 cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages (Macs). Histamines released from MCs in turn act on H1Rs and histamine 2 receptors (H2Rs) on Th1 and Th2 cells modulating type 1/type 2 cytokine production, leading to a hyperinflammatory environment. IL-4 and IL-13 released from MCs and Th2 cells act on macrophages and cause macrophage polarization leading to the release of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), which causes primed resident fibroblasts to differentiate into myofibroblasts that release collagen and other matric proteins leading to extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling and fibrosis. Also, the cytokines released from MCs, T cells, macrophages, and other cells might interact with immune and nonimmune cells to promote fibrosis independent of the myofibroblast transition. Combination treatment for MC inhibition that includes mast cell stabilizer (MCS) and H1R antagonist (H1RA) acts on multiple different cell types at multiple levels of these crucial aspects and regulates the tissue environment in a CP1-infected mouse prostate. [This model was created with BioRender.com.]