Figure 1.
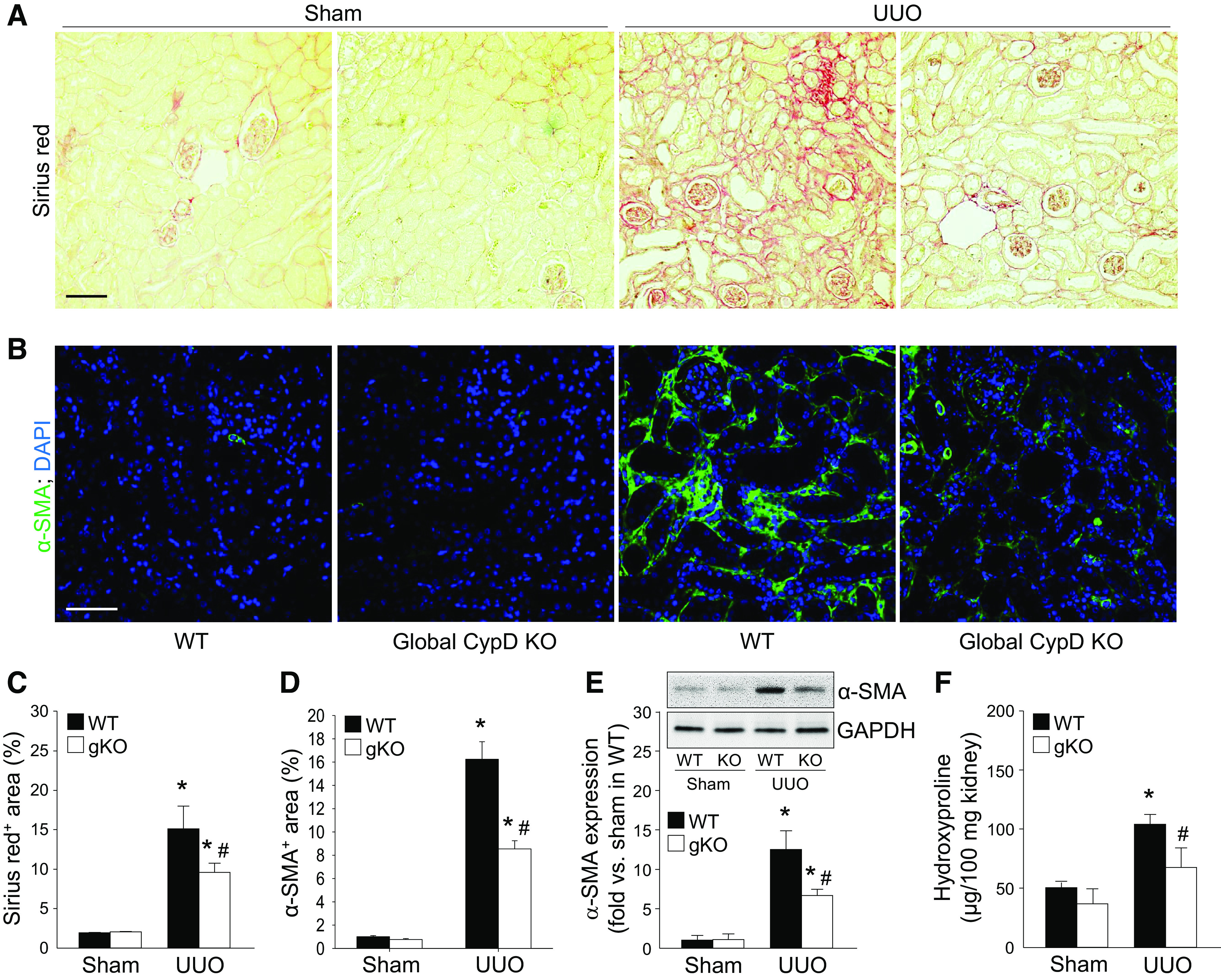
Prevention of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced kidney fibrosis by genetic deletion of cyclophilin D (CypD). Wild-type (WT) and global CypD knockout (KO) (gKO) mice were subjected to UUO or sham operation for 7 days. A and B: paraffin-embedded kidney sections were used to carry out Sirius red stain for collagen deposition (A) and immunofluorescent stain for evaluating α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), a marker of myofibroblasts (n = 5 or 6) (B). C and D: data for Sirius red-positive collagen deposition (red color; C) and α-SMA-positive area (green color; D) were quantified from five randomly chosen fields per kidney (n = 5 or 6). DAPI was used for counterstaining. Expression levels were evaluated using Image J software. E: expression of α-SMA was examined by Western blot analysis using specific antibodies. The Western blot bands were used as representative (n = 5). Anti-GAPDH antibody was used as a loading control. Expression levels were evaluated using ImageJ software. F: total collagen levels were evaluated by hydroxyproline assays in kidney lysates. Scale bars = 50 µm. Data are expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05 vs. sham; #P < 0.05 vs. WT UUO.
