Figure 2.
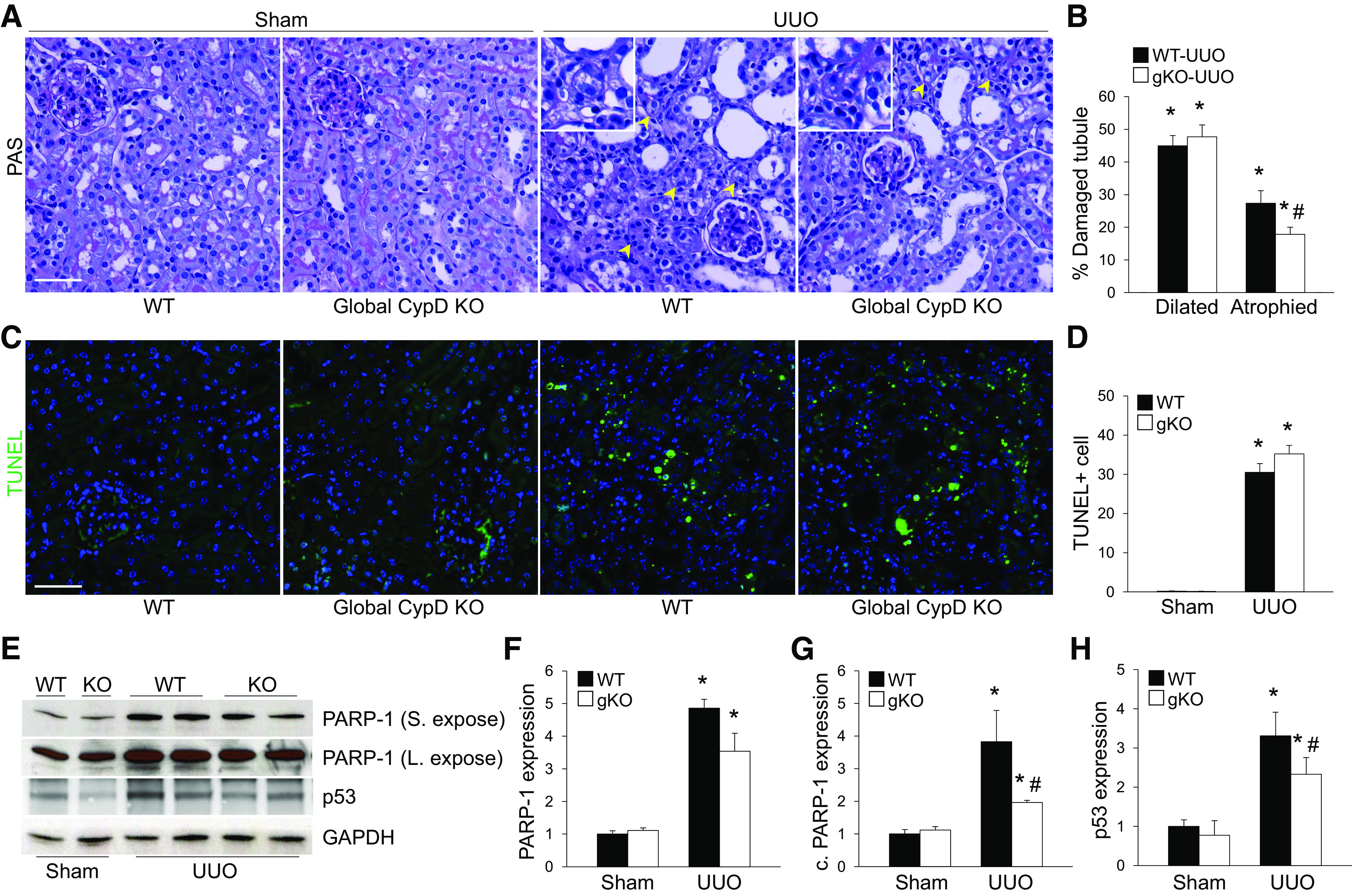
Global cyclophilin D (CypD) knockout (KO) (gKO) inhibits kidney tubular injury and atrophy during unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Wild-type (WT) and global CypD KO mice were subjected to UUO or sham operation for 7 days. A and C: paraffin-embedded kidney sections were used to carry out periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain (A) for evaluating histopathology and TUNEL stain (C) for evaluating tubular apoptotic cell death (n = 5 or 6). Yellow arrowheads indicate atrophied tubules. B: percent ratios of atrophied and dilated tubules to total tubules were calculated from 100 tubules in 5 randomly chosen fields per kidney (n = 5 or 6). D: numbers of TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells (green) were counted from 5 randomly chosen fields per kidney (n = 5 or 6). DAPI (blue) was used for counterstaining. E: expression levels of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP-1) and p53 were examined by Western blot analysis (n = 5), and representative Western blots are shown. F−H: quantification for PARP-1 and p53 was performed. Levels of PARP-1 were expressed by PARP-1 and cleaved PARP-1 (c. PARP-1) separately. Anti-GAPDH antibody was used as a loading control. Expression levels were evaluated using ImageJ software. Scale bars = 50 µm. Data are expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05 vs. sham; #P < 0.05 vs. WT UUO. S. expose, short exposure; L. expose, long exposure.
