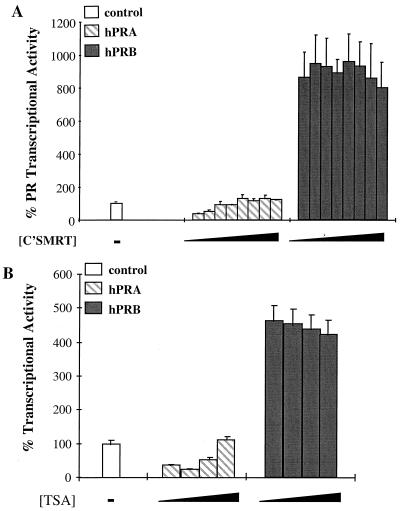
FIG. 9.
Inactivation of the nuclear receptor silencer SMRT does not convert hPRA to a transcriptional activator. (A) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with 1.5 μg of 2XPRE-TK-LUC, 50 ng of pBKC-βgal, either 52 ng of pBKC-hPRB, 48 ng of pBKC-hPRA, or 46 ng of pBKC-RevTUP1, and increasing concentrations (from 0 to 1 μg) of Gal4-C'SMRT. Various amounts of pBKC-DBD were added to balance the amount of input Gal4DBD. pBSK-II was added to normalize the total DNA to 3 μg. The transcriptional activity of these vectors was assayed on a 2XPRE-TK-LUC reporter and measured after the addition of 10−7 M R5020. Transfections were normalized for efficiency as mentioned previously. R5020-mediated transcriptional activity in the presence of increasing concentrations C'SMRT was normalized to the no-ligand control for each concentration of C'SMRT used. Each data point represents the average of triplicate determinations (± standard error of the mean) from two separate experiments (n = 2). The control represents basal reporter activity in the presence of control vector and was set to 100%. (B) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with 1.5 μg of 2XPRE-TK-LUC, 50 ng of pBKC-βgal, either 50 ng of pBKC-hPRA or 48 ng of pBKC-Rev-TUP1, and various amounts of pBSK-II for a total of 3 μg. Transcriptional activity of the constructs was measured following the addition of 10−7 M R5020 alone or in combination with increasing concentrations (0, 10−8, 10−7, and 10−6 M) of the deacetylase inhibitor TSA. Transfections were normalized for efficiency as mentioned above. R5020-mediated transcriptional activity in the presence of increasing concentrations of TSA was normalized to the no-ligand control for each TSA treatment used. Each data point represents the average of triplicate determinations (± standard error of the mean) from two separate experiments (n = 2).