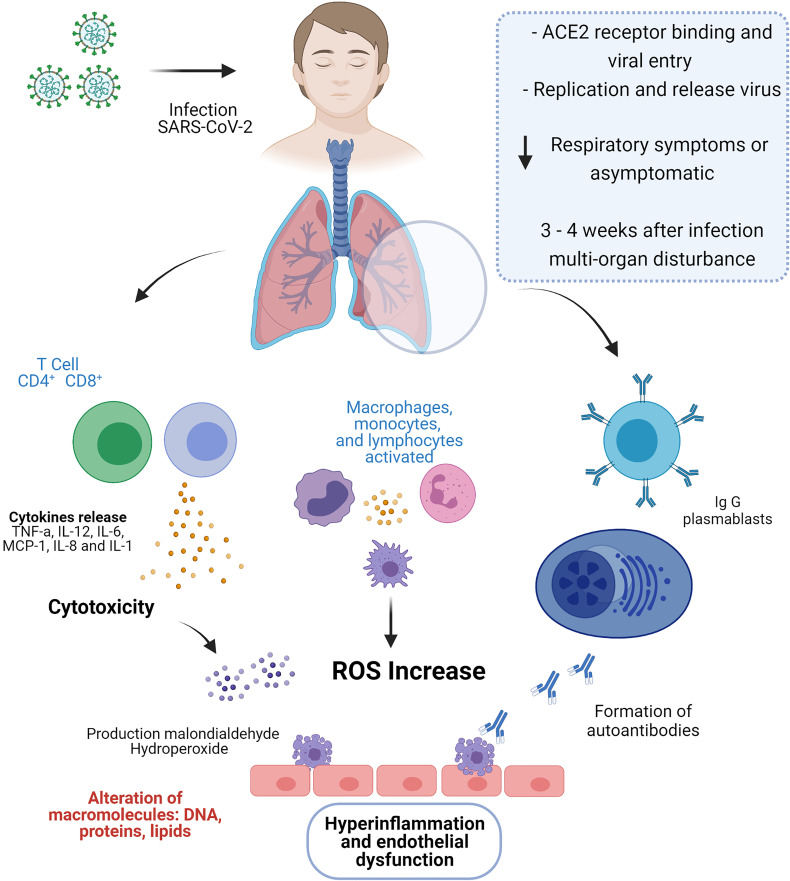
Figure 2.
In SARS-CoV-2 infection, the binding of the receptor ACE2 with the virus leads to entry into the host cell and its subsequent replication and release. During the active phase of COVID-19, MIS-C patients were asymptomatic or with mild respiratory symptoms; however, three to four weeks after exposure to SARS-CoV-2, children develop a multi-organ disturbance. MIS-C is characterized by strong activation of T lymphocytes leading to the release of a cytokine storm and increased cytotoxic activity. Furthermore, T cells, together with monocytes and macrophages, promote oxidative stress by increasing reactive oxygen species, which alter macromolecules such as DNA, proteins and lipids. Additionally, the presence of autoantibodies that recognize endothelial cells, promoting damage and contributing to endothelial dysfunction and multisystem inflammation typical of MIS-C. Figure created with BioRender, ©biorender.com.