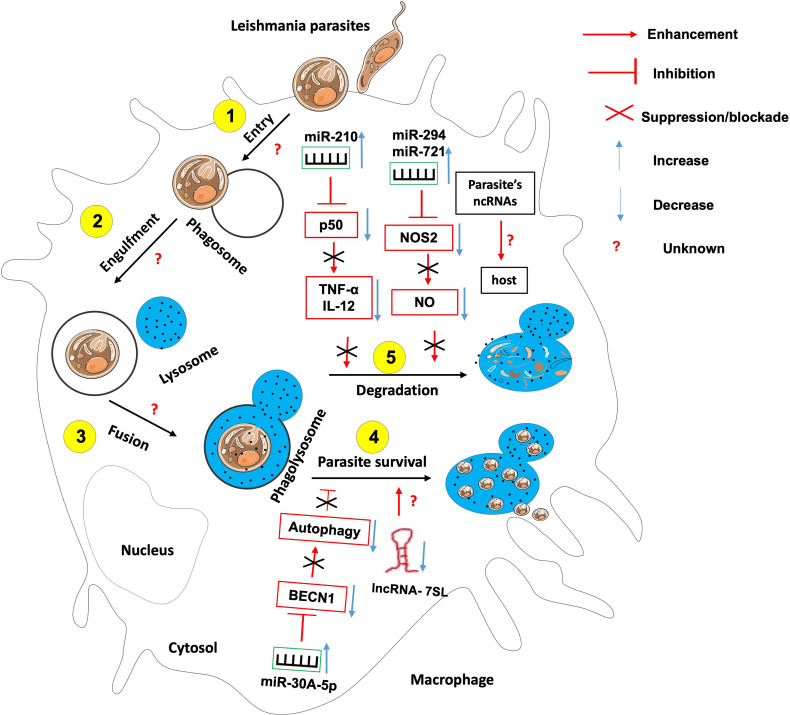
Figure 4.
The role of non-coding RNAs in the etiology of leishmaniasis. Most studies have identified ncRNAs that enhance host effector killing functions against leishmania parasites as well as those that favor parasite survival and persistence within the infected host. There is knowledge gap about 1- host ncRNAs that regulate the parasite entry within the host, its engulfment within phagosome and the fusion between phagosome and lysosomes; 2- the role of Leishmania-derived ncRNAs on the outcome of leishmania-macrophage interaction.