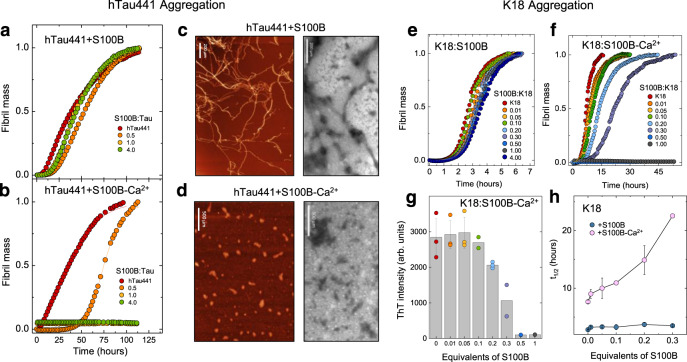
Fig. 4. S100B-Ca2+ inhibits full-length tau and K18-fragment aggregation.
a, b Fibril formation of 25 µM hTau441 (red) in 50 mM Tris, pH 7.4, in the absence (a) or the presence (b) of 1.1 mM CaCl2 at 37 °C under agitation in the presence of 0.5 (orange), 1.0 (yellow), and 4.0 (green) molar equivalents of S100B. Aggregation induced by 0.5 mg/mL heparin addition. c, d AFM (left) and TEM (right) imaging of end-time species of hTau441 aggregation in the absence (c) or the presence (d) of Ca2+ at 10 µM tau and at a S100B:tau molar ratio of 1. Scale bars, 200 µm (c) and 500 µm (d). Independent experiments of AFM and TEM morphological analysis were performed at least three times. e, f Fibril formation of 10 µM K18 (red) in 50 mM Tris, pH 7.4, in the absence (e) or the presence (f) of 1.1 mM CaCl2 at 37 °C under agitation in the presence of 0.01 (orange), 0.05 (yellow), 0.1 (green), 0.2 (light blue), 0.3 (purple), 0.5 (blue), 1.0 (gray), and 4.0 (dark blue) molar equivalents of S100B. Aggregation induced by 90 µg/mL heparin addition. Plots represent averaged normalized intensity curves obtained from three independent replicates for each of the tested conditions. g ThT intensity in arbitrary units (arb. units) of end-time point K18 aggregation in the presence of 1.1 mM CaCl2 (same color code); h half-time of K18 aggregation in the absence (blue) or the presence (light pink) of 1.1 mM CaCl2. Data are presented as mean values ± SD from n = 3 independent experiments except for samples with 0.1 and 0.3 equivalents of S100B for which n = 2. See Methods for details.