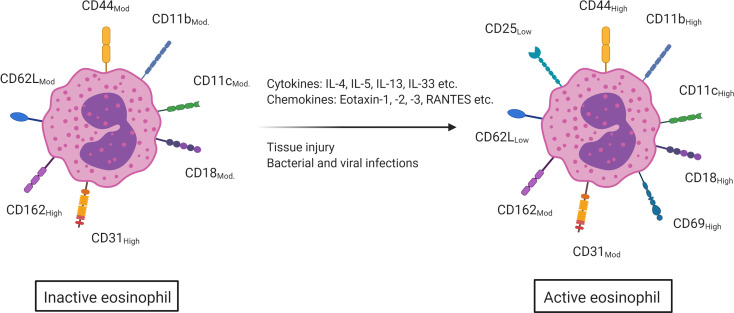
Figure 2.
Upon contact with several cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-33, etc.), chemokines (eotaxin-1,2 and -3, RANTES etc.) and via tissue damage and bacterial and viral infections, eosinophils will become activated. This activation is marked by an increased surface expression of CD18, CD44, CD11b and CD11c (moderate to high expression). CD25 and CD69 are not present on inactive eosinophils, but are on active eosinophils (low and high expression respectively). CD162 and CD31 on the other hand are highly expressed on inactive eosinophils but only moderately on active eosinophils and CD62L is moderately expressed on inactive eosinophils but becomes lowly expressed once the eosinophil is activated. This figure was created via biorender.com.