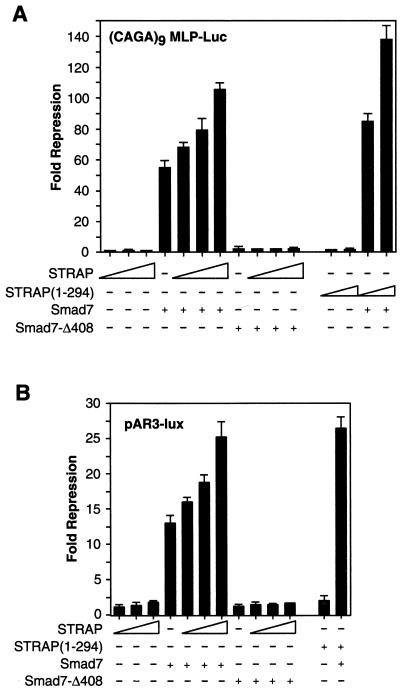
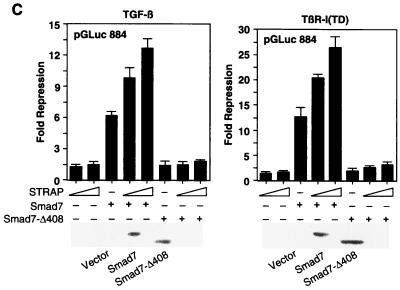
FIG. 2.
Functional synergy between STRAP and Smad7. (A) Synergistic inhibition of (CAGA)9 MLP-Luc reporter activity in response to TGF-β. HepG2 cells were transfected with a (CAGA)9 MLP-Luc reporter (0.3 μg) containing nine copies of Smad3/Smad4 binding sites, Smad7 constructs, increasing amounts of STRAP, and increasing amounts of STRAP(1-294) (0.5 and 1 μg). TGF-β signaling was initiated by expression of TβR-I(T204D). Luciferase assays were performed as described for Fig. 1A. (B) STRAP and Smad7 synergistically block an immediate-early response to TGF-β. HepG2 cells were cotransfected with pAR3-lux (0.3 μg), FAST2 (15 ng), Smad7 constructs, STRAP(1-294) (1 μg), and increasing amounts of STRAP as indicated. Cells were treated with or without TGF-β (100 pM) for 20 h prior to lysis and then analyzed for luciferase activity. (C) Synergistic inhibition of TGF-β-induced PAI-1 promoter activity by STRAP and Smad7. HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with pGLuc 884 reporter (0.25 μg) (9), HA-tagged Smad7 constructs, and increasing amounts of STRAP. TGF-β signaling was initiated either by treatment of the cells with 100 pM TGF-β (left) or by coexpression of TβR-I(TD) (right). Luciferase assays were performed as described for Fig. 1A. Expression of Smad7 proteins were confirmed by direct immunoblotting of total cell lysates, made for luciferase assays from cells transfected with either vector or coding sequences for Smad7 or the Smad7-Δ408 construct, with anti-HA antibodies.