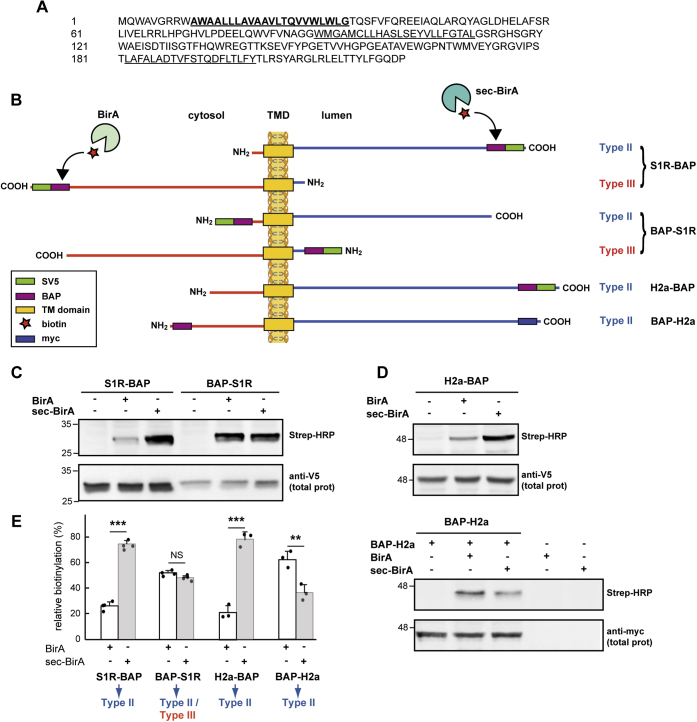
Figure 1.
C-terminal BAP-tagging of the S1R suggests a type II membrane topology and mixed topology by N-terminal tagging.A, sequence of human S1R. Underlined are hydrophobic stretches, in bold a region with a high probability prediction for a TMD and not bold for additional lower probability TMDs. B, a scheme of BAP-tagged S1R constructs S1R-BAP and BAP-S1R adopting type II or type III orientations, and their biotinylation in each case by cytosolic BirA or luminal sec-BirA. For comparison, BAP-tagged constructs of H2a, which has a known type II topology. Each construct has an SV5 tag adjacent to the BAP tag, except for BAP-H2a, which has a BAP tag at the N-terminus and a myc tag at the C-terminus. C, S1R-BAP or BAP-S1R was expressed in HEK293 cells together with BirA or sec-BirA as indicated, and cells were incubated with biotin. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot with anti-V5, showing total expression or Strep-HRP to detect biotinylated species. On the left, the migration of MW markers in kDa. D, similar to (B) but with cells expressing H2a-BAP (upper panels) or BAP-H2a (lower panels). Additional controls show expression of only BirA or sec-BirA. E, relative biotinylation was calculated by dividing the Strep-HRP signal obtained for each sample by the total protein signal, the results attained for each protein with BirA + sec-BirA were then considered 100% for comparison purposes. The graph represents an average of four independent experiments for S1R constructs and three for H2a ±SD, p values ∗∗ =0.007, ∗∗∗ <0.0002, NS: nonsignificant >0.05. Student's t test (paired, two-tailed).