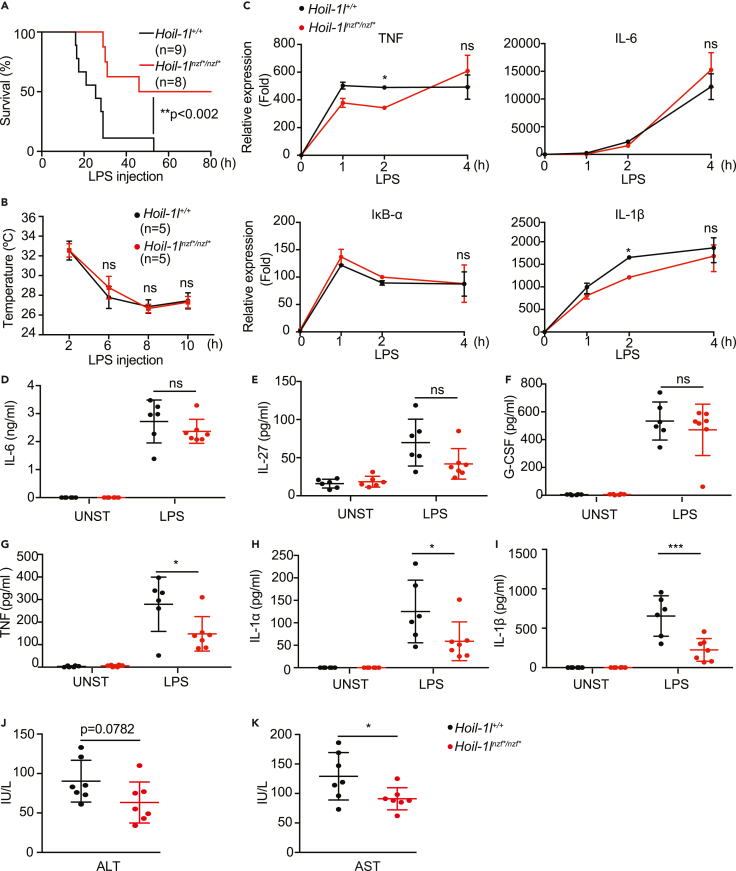
Figure 4.
Hoil-1lnzf∗/nzf∗mice are more resistant to LPS-induced septic shock than wild-type mice
(A) Survival curve of Hoil-1l+/+ (n = 9) and Hoil-1lnzf∗/nzf∗ (n = 8) mice upon LPS injection. Hoil-1l+/+ (n = 9) and Hoil-1lnzf∗/nzf∗ (n = 8) mice were injected with 30 mg/kg of LPS, and the survival was monitored up to 80 h.
(B) Body temperature of Hoil-1l+/+ (n = 5) and Hoil-1lnzf∗/nzf∗ (n = 5) mice upon LPS injection (30 mg/kg) monitored over time.
(C) qRT-PCR to monitor mRNA transcript levels of TNF, IL-6, IκB-α, IL-1β determined in Hoil-1l+/+ and Hoil-1lnzf∗/nzf∗ BMDMs treated with LPS (10 ng/mL) for the indicated time. Normalization was done to β-actin.
(D–I) ELISA to monitor IL-27, G-CSF, IL-6, TNF, IL-1α, and IL-1β levels in the serum of control and LPS-injected (30 mg/kg) mice. Samples for LPS-injected mice were collected after 12 h of LPS injection. Unstimulated (UNST): Hoil-1l+/+ (n = 6) and Hoil-1lnzf∗/nzf∗ (n = 6), and LPS-injected (LPS): Hoil-1l+/+ (n = 6) and Hoil-1lnzf∗/nzf∗ (n = 7).
(J and K) ALT and AST levels in the sera of Hoil-1l+/+ (n = 7) and Hoil-1lnzf∗/nzf∗ (n = 7) mice 12 h post LPS injection (30 mg/kg). (A) Log-rank (Mantel-Cox test) ∗∗p value = 0.0018. (B-I) Data are represented as mean ± SD, ANOVA. (C) Representative data from three independent experiments, n = 3, ∗p value ≤0.05. (D-I) ∗p value ≤0.05, ∗∗∗p value ≤0.001. (J-K) Data are presented as mean ± SD, Student’s t, ∗p value ≤0.05.