FIGURE 2.
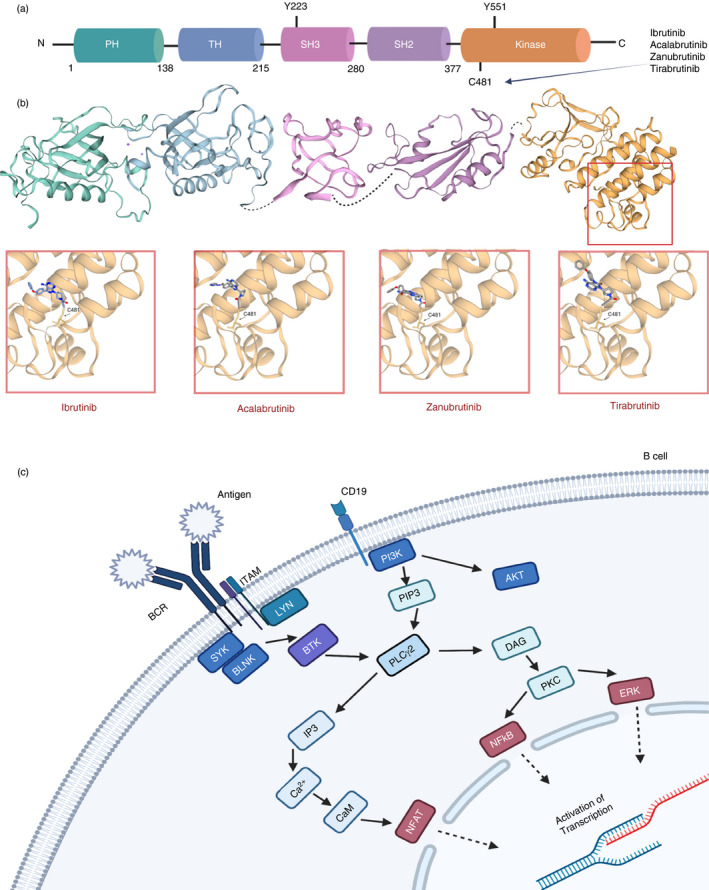
Structural overview of BTK and BTK inhibitors and its position within the B‐cell receptor signalling pathway. (a) The 77 kDa BTK protein consists of 659 amino acids, which make up the five domains for protein interaction. The 2 critical sites within the protein are Y223 and (SH3 domain) and Y551 (kinase domain: orange/yellow domain). (b) BTK inhibitors act through the binding to one of the proteins interacting domains and blocking BTK’s catalytic action. The main site of binding for current covalent inhibitors is the C481 residue within the kinase domain. This includes ibrutinib and second‐generation inhibitors acalabrutinib, zanubrutinib and tirabrutinib as depicted at the 3D models (data obtained from SWISS‐MODEL repository by the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics [101] for the crystal structures of each BTK domain and then NCBI's PubChem database for the line structures for each inhibitor [102]). (c) A simplified version of B‐cell receptor signalling pathway and BTK position within it [103]
