FIGURE 3.
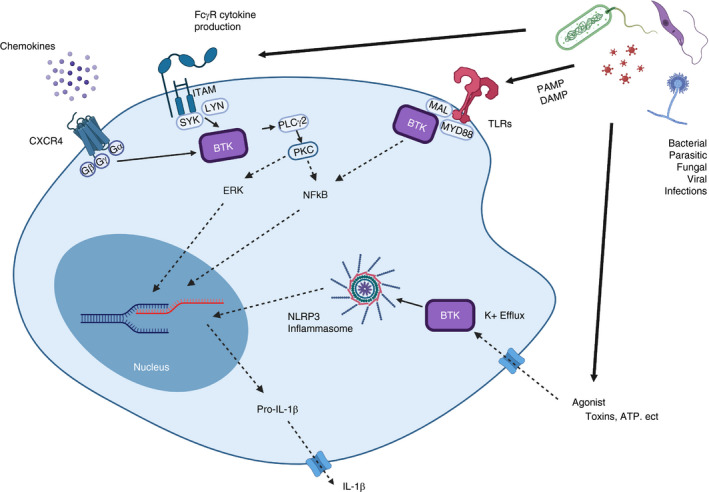
Overview of the various roles of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) in innate immunity. Chemokine receptor (CXCR4) activation upon chemokine binding leads to the dissociation of G proteins made up of Gα, Gβ and Gy subunits and downstream activation of BTK. ITAM‐containing (and also ITIM‐containing) Fc receptor crosslinking leads to activation of SYK and in turn BTK. Toll‐like receptors (TLRs) are activated by pathogen‐associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and‐damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Activation of TLRs is followed by recruitment of MYD88. BTK in turn interacts with MYD88 leading to activation of transcription factors such as NF‐кB. BTK is a direct regulator in the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Efflux of K+ into the cell leads to phosphorylation of BTK, most likely by SYK, followed by activation. This phosphorylation promotes assembly of the inflammasome and leads to the cleavage and secretion of IL‐1β [103]
