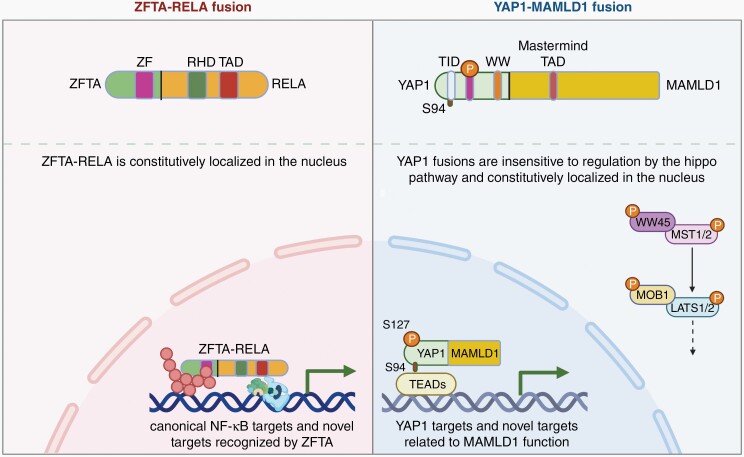
Fig. 1.
Schematic of known oncogenic mechanisms of ZFTA-RELA (a) and YAP1-MAMLD1 (b) fusions in supratentorial ependymomas. ZFTA-RELA fusion retains portion of ZFTA with zinc-finger (ZF) domain and portion of RELA with Rel homology domain (RHD) and transcriptional activation domain (TAD), resulting in constitutively active and nuclear localized fusion product and expression of canonical NF-kB and novel targets. YAP1-MAMLD1 fusion retains N-terminal YAP1 with S94 phosphorylation site within the YAP1-TEAD interaction domain (TID), S127 phosphorylation site, and WW domain (WW) along with C-terminal MAMLD1 containing nuclear localization signal (NLS) and transcriptional activation domain (TAD). YAP-MAMLD1 fusion is resistant to regulation by Hippo kinase cassette and constitutively nuclear, resulting in transcriptional activity of YAP1 and MAMLD1 targets. Created with BioRender.com