Figure 1 .
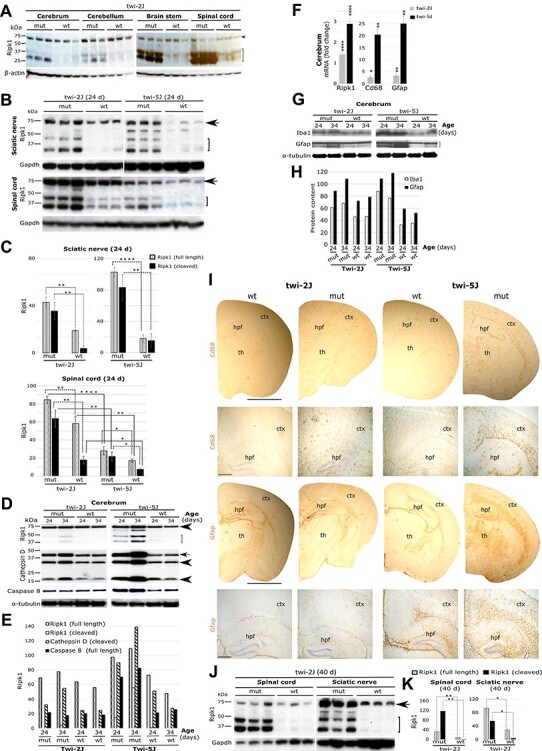
Spatiotemporal expression of Ripk1 in murine models of Krabbe disease. (A) Immunoblots of Ripk1 in different twi-2J CNS structures at HEP; arrowhead (full-length Ripk1), bracket (cleaved Ripk1); (B) Immunoblots of Ripk1 in sciatic nerve and spinal cord from twi-2J and -5J at P24; (C) Ripk1 densitometry of full-length and cleaved species relative to Gapdh in B; (D) Immunoblots of Ripk1, cathepsin D and caspase-8 (55 kDa, uncleaved) in twi-2J and -5J cerebrum at P24 and P34. Cathepsin D forms: arrow (intermediate), arrowheads (mature); (E) Densitometry of Ripk1, cathepsin D and caspase-8 relative to α-tubulin in D; (F) RT-qPCR of total RNA for Ripk1 and gliosis markers Cd68 and Gfap in twi-2J and -5J cerebrum at P24; (G) Immunoblots of Iba1 and Gfap in twi-2J and -5J cerebrum at P24 and P34; (H) Densitometry of Iba1 and Gfap relative to α-tubulin in G; (I) Bright field images of Cd68 IHC-stained cerebrum sections from twi-2J and -5J at their HEP, 40 and 24 days, respectively; (J) Immunoblots of Ripk1 in spinal cord and sciatic nerve in twi-2J at the HEP; (K) Densitometry of Ripk1 relative to Gapdh in J. For immunoblotting, 75–150 μg protein homogenate was loaded per lane. Blots were stripped of the first antibody and re-probed. Note, of the cleaved Ripk1 species only the lower form was used for densitometry as the upper one is often difficult to detect in wt animals. Cluster of differentiation 68 (Cd68), Glial fibrillary acidic protein (Gfap), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase (Gapdh), Receptor-interacting serine–threonine kinase 1(Ripk1), mutant (mut), wild type (wt), cerebral cortex (ctx), hippocampal formation (hpf) and thalamus (th). Scale bar: 2 mm for full size half cerebrums, and 200 μm for magnified views below. Student’s t-test; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001
