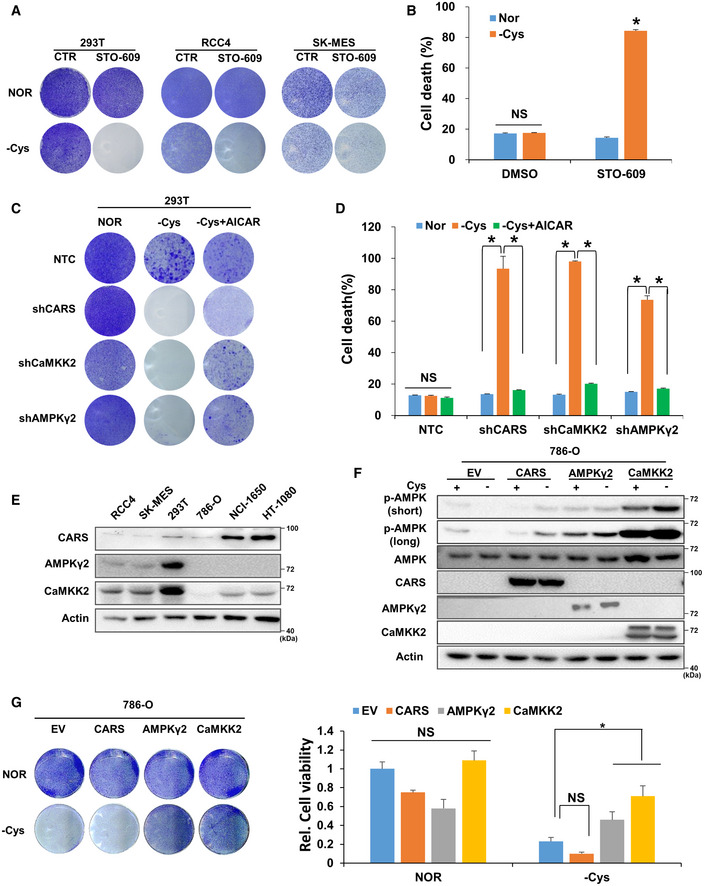
Figure 4. The CARS‐CaMKK2‐AMPK axis promotes cell survival when cystine is eliminated.
-
AThe crystal violet assay was performed in cystine‐deficient medium‐cultured 293T, RCC4 and SK‐MES cells with or without 1 µg/ml STO‐609 for 24 h.
-
BThe cell death level was determined in 293T cells with the same treatment conditions as in Fig 4A. Data are presented as the mean (± SD) of three independent experiments. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05 [two‐tailed Student’s t‐test], compared with the indicated groups.
-
C, DThe crystal violet assay (C) and apoptosis rate assay (D) were performed in 293T cells transfected with shRNAs targeting NTC, CARS, CaMKK2 or AMPKγ2 and further treated with cystine‐deficient medium for 24 h with or without 1 mM AICAR. Data are presented as the mean (± SD) of three independent experiments. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05 [two‐tailed Student’s t‐test], compared with the indicated groups.
-
EWB analysis of CARS, CaMKK2 and AMPKγ2 protein expression in RCC4, SK‐MES, 293T, 786‐O, NCI‐1650 and HT1080 cells. Actin served as the loading control.
-
F, GWB analysis of p‐AMPK, total AMPK, CARS, AMPKγ2 and CaMKK2 protein expression (F) and a crystal violet assay were performed (G, left) with 786‐O cells transfected with Flag‐EV, Flag‐CARS, Flag‐CaMKK2 or Flag‐AMPKγ2 and further treated with cystine‐deficient medium for 8 h. Actin served as the loading control. After scanning, 20% glacial acetic acid was added to dissolve the crystal violet, and the absorbance of each well was measured at 570 nm (OD570) to calculate relative cell viability (G, right). Data are presented as the mean (± SD) of three independent experiments. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05 [two‐tailed Student’s t‐test], compared with the indicated groups.
Source data are available online for this figure.
