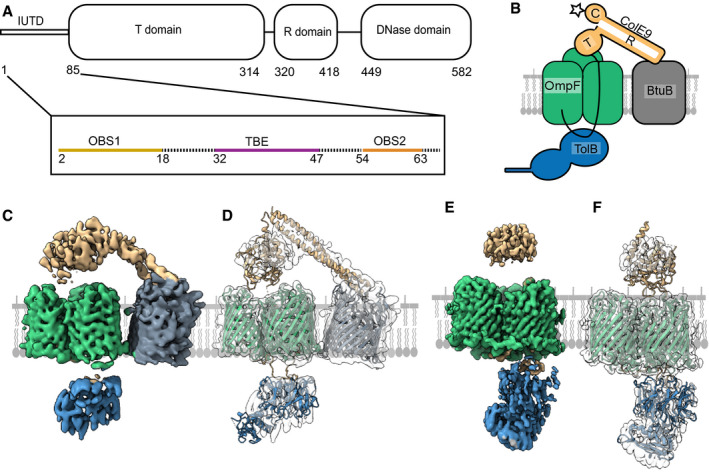
Schematic of the ColE9 sequence showing its constituent domains: an intrinsically unstructured translocation domain (IUTD) at the N‐terminus is followed by three structured domains involved in translocation (T), receptor (R) binding and cytotoxicity (C). The IUTD houses three linear protein‐protein interaction epitopes, two OmpF‐binding sites (OBS1, OBS2) flank a TolB‐binding epitope (TBE). Residue numbers denote position in ColE9 sequence.
Cartoon of the ColE9 OM translocon. ColE9 (orange) exploits the vitamin B12 transporter BtuB (grey) as its extracellular receptor and the porin OmpF (green) for threading its N‐terminal IUTD (solid black line) through to the periplasm where it captures TolB (blue). Star represents the primary site on the ColE9 DNase domain (K469C) where fluorophores were covalently attached throughout this study.
Cryo‐EM map of the fully assembled ColE9 translocon, with local resolution range 4.5–16 Å. Component proteins are coloured as in panel B. The structure shows extracellular ColE9 creating a protein bridge between the two OMPs, BtuB and OmpF. The β‐barrel of BtuB is tilted 35° relative to that of OmpF. TolB is located on the periplasmic side of OmpF, with no associations to BtuB. ColE9 and TolB regions of the map have weaker density than those of the β‐barrels.
Model of the intact ColE9 translocon generated after docking and rigid‐body refinement of individual structures of ColE9 residues 85–580 (PDB ID 5EW5), OmpF (3K19), BtuB (PDB ID 2YSU) and TolB (PBD ID 4JML).
Cryo‐EM map of the partial ColE9 translocon with an average resolution of 3.7 Å, which has density consistent with OmpF, TolB, and ColE9 residues 3–314. Map is coloured based on component parts shown in panel B. TolB is much better resolved here than in the full translocon map in panel C, although ColE9 density is weaker. ColE9 and TolB density align on the extracellular and periplasmic side of OmpF, respectively.
The refined structure of the partial translocon, generated by docking and refinement of ColE9 residues 85–580 (PDB ID 5EW5), OmpF (PDB ID 3K19) and TolB‐ColE9 TBE (PDB ID 4JML). ColE9 residues 3–67 were built de novo.