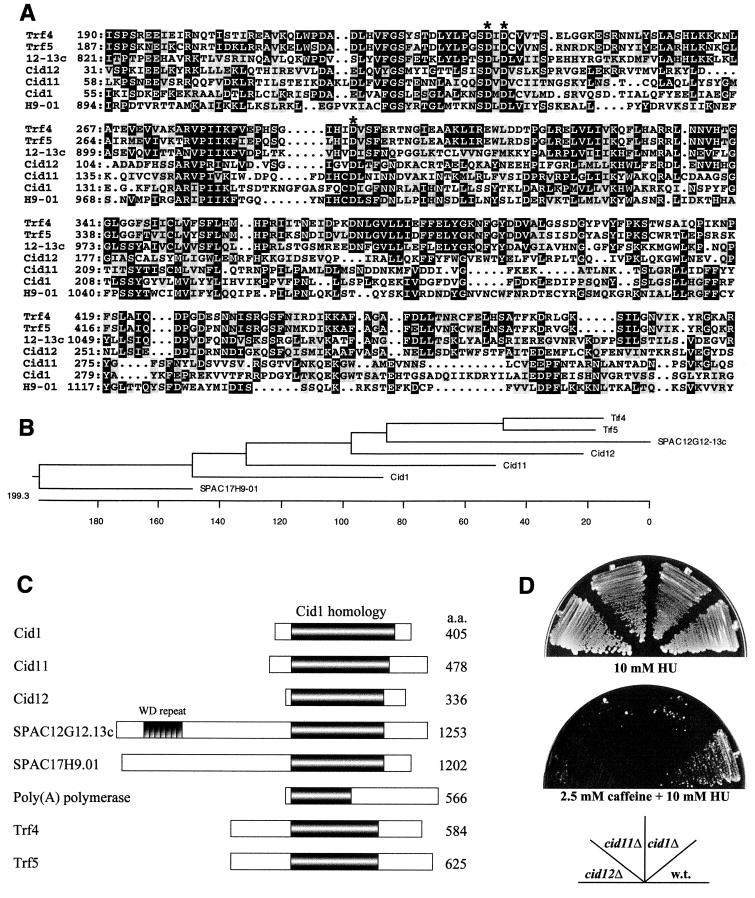
FIG. 6.
Cid1 belongs to a novel protein family in S. pombe. (A) Alignment of the predicted protein sequences of Cid1 and related proteins in S. pombe and S. cerevisiae. Only the region of significant similarity to Cid1 (approximately 300 amino acid residues) is shown in each case, with amino acid residue numbers given on the left. 12-13c denotes the predicted product of SPAC12G12-13c, and H9-01 denotes the predicted product of SPAC17H9-01. Amino acid residues found at the same position in three or more of the aligned sequences are shaded in black, and conservative substitutions are highlighted in grey. The conserved aspartate triad residues are indicated by asterisks. (B) Cladogram showing the relationship between Cid1 family members in S. pombe and the Trf4 and Trf5 proteins of S. cerevisiae. The length of each pair of branches represents the distance between sequence pairs. Units indicate the number of substitution events. (C) Schematic representation of the overall structural similarity between Cid1, Cid11, Cid12, SPAC12G12.13c, SPAC17H9.01, and poly(A) polymerase from S. pombe and Trf4 and Trf5 from S. cerevisiae. The extent of the region of significant similarity between these proteins is indicated by the shaded area, and the location of the seven tandem WD repeats in SPAC12G12.13c is also shown. (D) Deletion of any one of the smaller cid1-related genes results in sensitivity to HU in the presence of low-dose caffeine. Strains HM123 (wild type [w.t.]), cid1Δ, cid11Δ, and cid12Δ were streaked as indicated onto YPD agar containing 10 mM HU or 2.5 mM caffeine plus 10 mM HU. The plates were photographed after 7 days of incubation at 30°C.