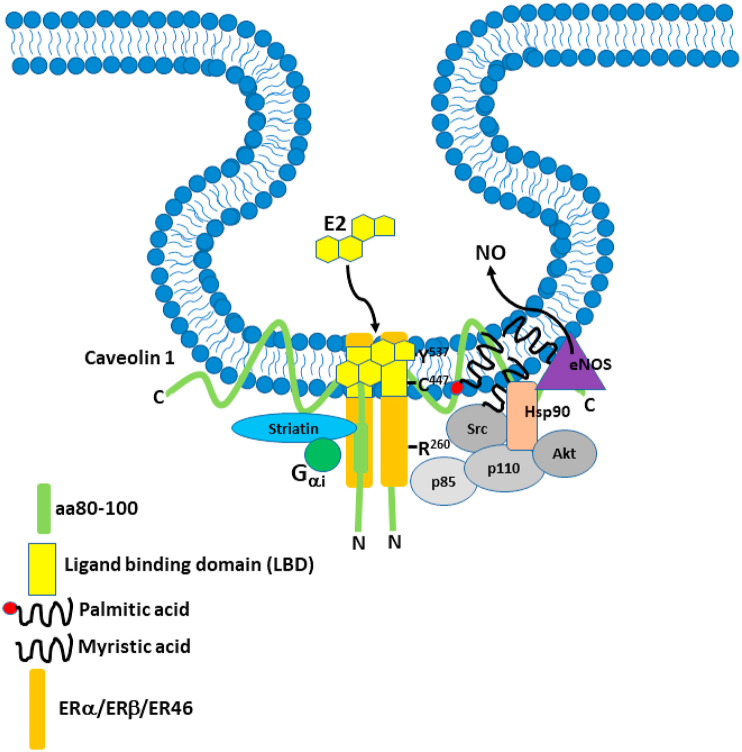
Fig. 2.
The Estrogen Receptor Complex. ERα, ERβ or ER46 is complexed with Gαi, c-Src TK, PI3K, Akt, Hsp90 and eNOS in caveolae, where it assembled on caveolin 1 with striatin. In this depiction ER is shown assembled on caveolin 1 and spanning the membrane. There is evidence that ER presents an ectodomain, although it is not clear whether the C-terminal ligand binding domain is extracellular or in the membrane, because E2 is lipid soluble and can cross the membrane. ER assembles on the aa80-100 region of the caveolin 1 N-terminus. ER is palmitylated on Cys447 which anchors it to the membrane. The recruitment of Src TK and PI3K can occur on the methylated Arg260. However, phosphorylation of Tyr537 has also been reported to recruit Src TK via its SH2 group, although this would probably occur in a model where ER is tethered to the inside of the membrane rather than spanning the membrane. C-Src tyrosine kinase is also myristylated on Gly2. In endothelial cells estrogen (E2) binding to this complex rapidly initiates a signaling cascade leading to the activation of eNOS and NO production. P85 and p110 are regulatory subunits of PI3K. Rapid signaling is essential for inhibiting VSMC proliferation, inducing vasorelaxation and endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Adapted from various sources, including (Kim and Bender, 2005).