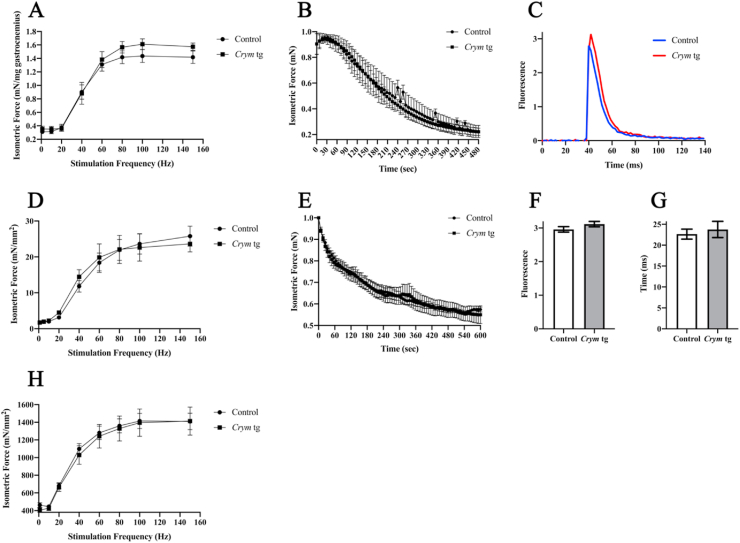
Fig. 3.
Contractile properties of Crym tg muscle. Force frequency curves (A, B, D, E, H) of gastrocnemius (A, B), soleus (D, E), and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) (H). Force was normalized to gastrocnemius muscle weight (A) or to soleus or EDL cross-sectional area (D, H). For fatigue, force was normalized to peak force (B, E). Ca2+ transients in isolated myofibers (C, F, G). C. Representative Ca2+ transient evoked by a voltage pulse, visualized with Rhod2. Blue, control; red, Crym tg. F. Maximal amplitudes of the Ca2+ transients. (n = 100). G. Mean time constants for the decay of the transients (n = 100). Statistics utilized the Student's t-test for Ca2+ measurements (F, G) or the Holm-Šídák test on the gastrocnemius (n = 5; A, B), soleus (control n = 4, Crym tg n = 5; D, E), or EDL (control n = 6, Crym tg n = 5; H) at α = 0.05. All error bars show standard error. The results show no statistically significant differences in any of these measurements.