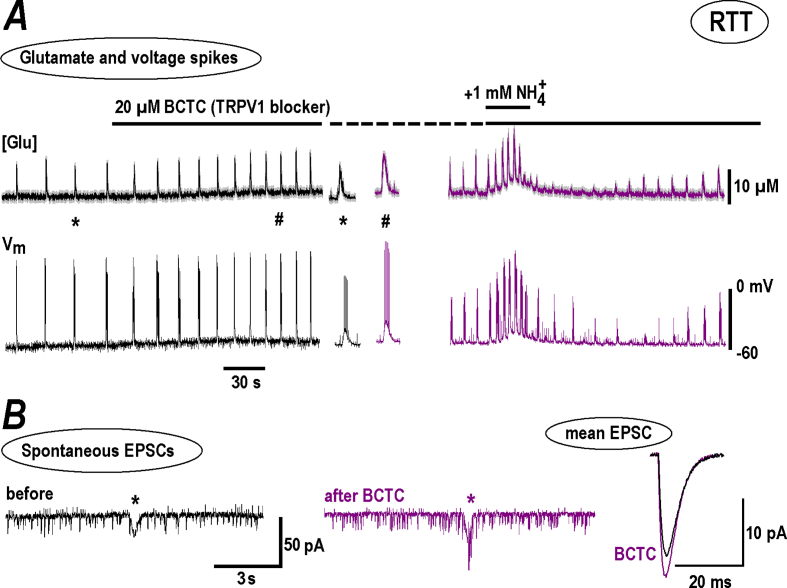
Fig. 8.
Modulation of NH4+effects in RTT slices by TRPV1 channel blocker, BCTC. The experiments with BCTC were conducted in a similar way as presented in Fig. 4, Fig. 6 for amiloride and SKF, respectively. A – BCTC increased the amplitude and frequency of glutamate spikes and AP bursts (left panel) and potentiated subsequent response to NH4+ (right panel). B – Continuous traces show spontaneous EPSCs and include single synaptic drive (asterisk). BCTC increased EPSC amplitude and the frequency was unchanged (the statistics is given in Fig. 5). Mean EPSC on the right demonstrate some increase in the amplitude with the time-course unchanged, consistent with unaltered electrotonic conduction. The traces obtained in the presence of BCTC are violet-coded. The mean data from respective experiments are summarized in Fig. 5.