Figure 1. Generation of OV-IL15C and quantification of the IL-15/IL-15Rα complex produced by OV-IL15C infection of GBM cells.
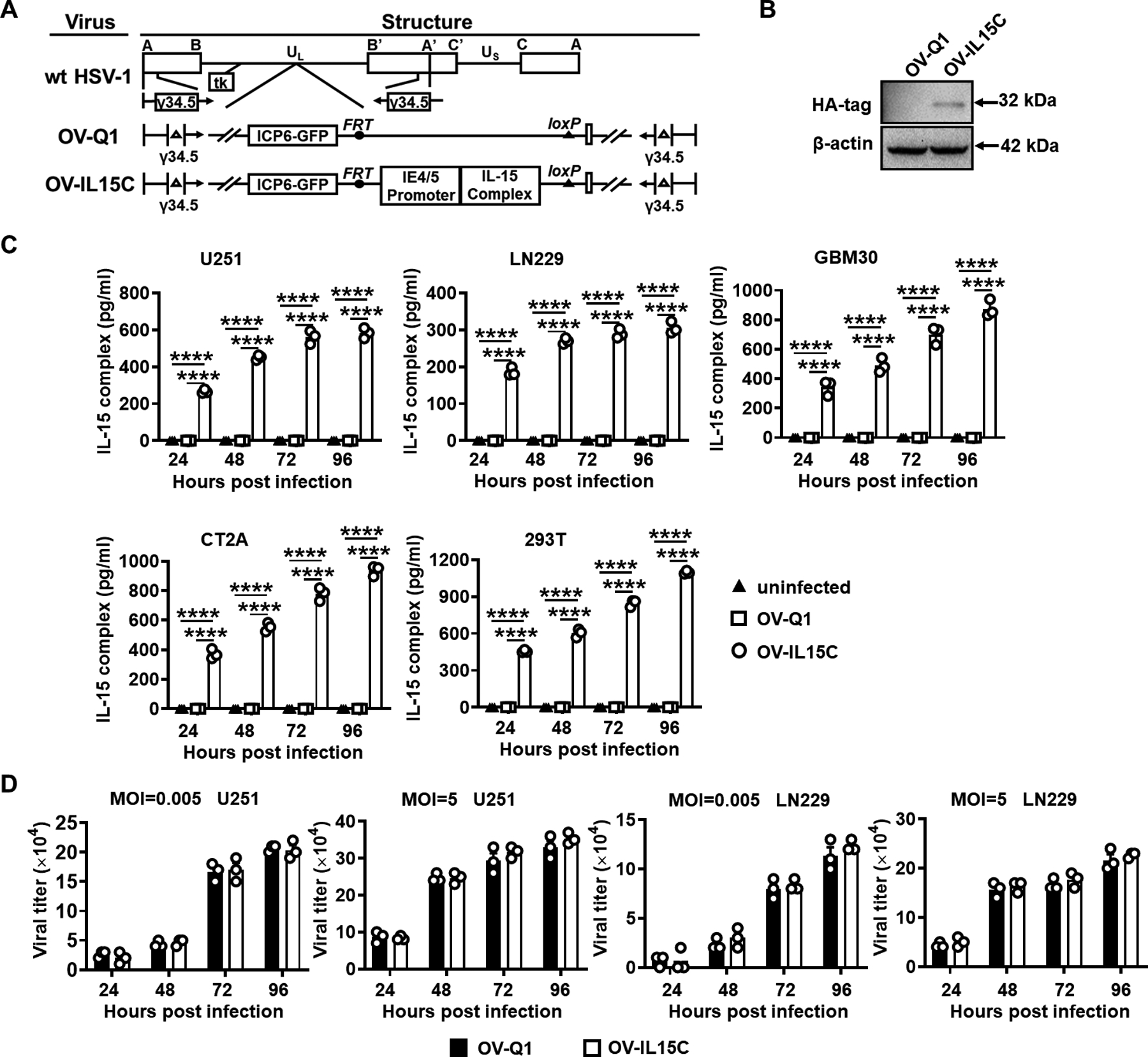
A, Schematic maps of oncolytic viruses used in this study. First: genetic map of wild-type HSV-1 (wt HSV-1). Second: genetic map of the parental oHSV control (OV-Q1) with deletion of γ34.5, dysfunction of ICP6, and insertion of the GFP gene. Third: genetic map of the new oHSV (OV-IL15C) showing the insertion of the human IL-15 and IL-15Rα sushi domain driven by the viral pIE4/5 promoter. B, Immunoblotting to test the expression of the human IL-15/IL-15Rα complex at the protein level. 293T cells were infected by OV-Q1 or OV-IL15C at a MOI of 2. Two days later, cell lysis was collected and used for detection of the HA-tagged IL-15/IL-15Rα complex by immunoblotting with an expected size. β-actin was used as a sample loading control. C, ELISA for the human IL-15/IL-15Rα complex quantification. GBM cell lines (human cell lines U251, LN229, GBM30, murine GBM cell line CT2A) and 293T cells were infected with OV-Q1 or OV-IL15C at a MOI of 0.05. Supernatants from different groups were collected for quantification by a DuoSet ELISA kit. P values correct for ordinary one-way ANOVA using Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test. Values are presented as mean ± SEM. ****, P < 0.0001. D, Viral production capacity test. Human GBM cell lines U251 or LN229 were seeded in a 96-well plate and infected by OV-Q1 or OV-IL15C at different MOIs (MOI=0.005 unsaturated or 5 saturated). Twenty-four hours, 48 hours, 72 hours, and 96 hours post infection, GFP-positive plaques were counted with a Zeiss fluorescence microscope.
