Figure 3. Enhancement of GBM virotherapy in vivo by OV-IL15C co-administered with human CD8+ T cells in a xenograft GBM mouse model.
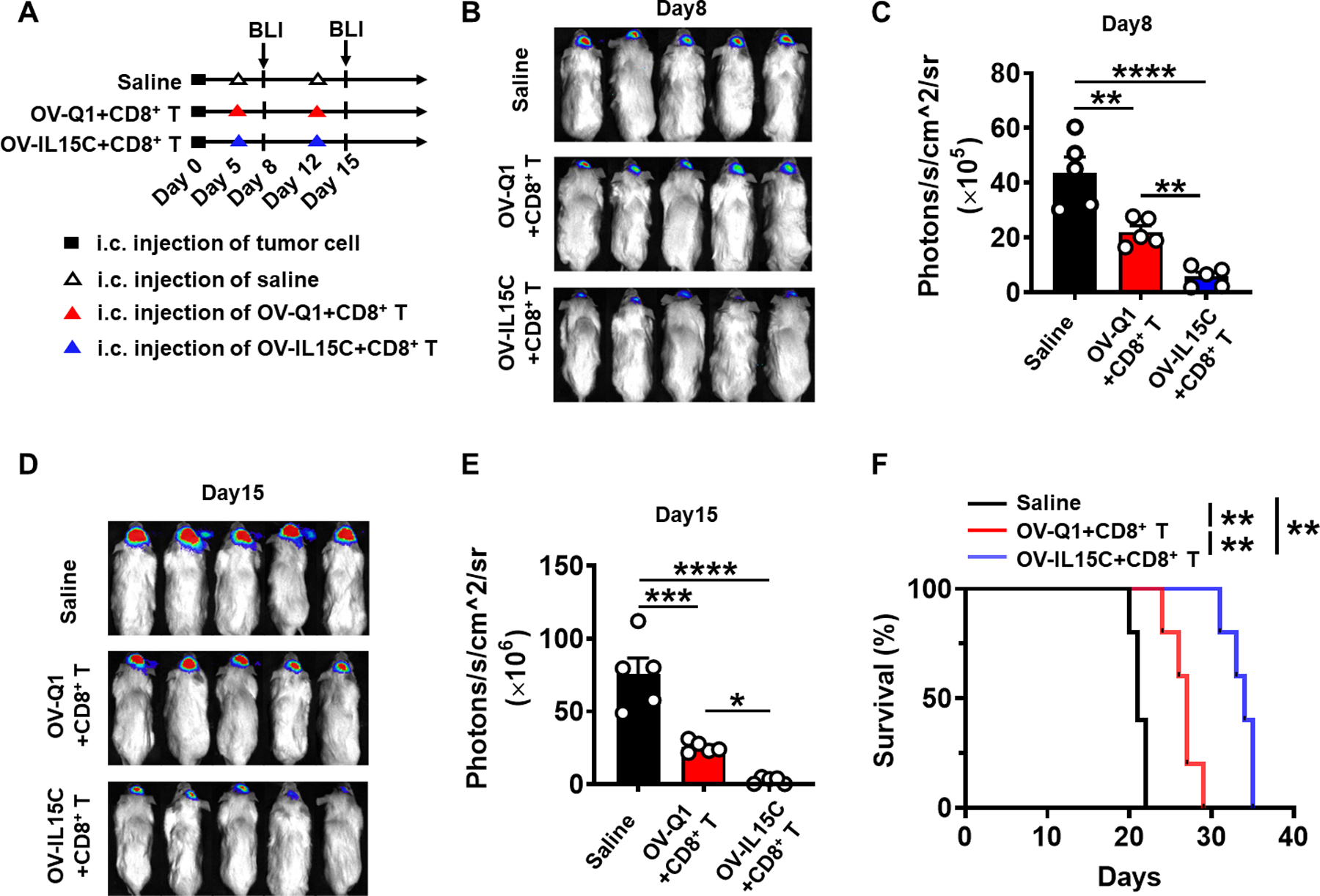
A, Experimental timeline for in vivo study. An orthotopic xenograft GBM mouse model was established by intracranial injection of 1 × 105 luciferase-expressing GBM30 cells (GBM30-luc) into the brain of NOD/SCID/IL-2rg (NSG) mice on day 0. On days 5 and 12, mice were intratumorally injected with 2 × 105 pfu of OV-Q1, OV-IL15C, or saline. The two virus groups were co-administered with 1 × 106 activated CD8+ T cells. n=5 animals for each group. B, On day 8, bioluminescence imaging (BLI) to check brain tumor growth. C, Quantification of BLI in B. P values correct for ordinary one-way ANOVA using Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test. Values are presented as mean ± SD. **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001. D, BLI to check brain tumor growth on day 15. E, Quantification of BLI in D. P values correct for ordinary one-way ANOVA using Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test. Values are presented as mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. F, Survival of GBM30-luc bearing mice treated with OV-Q1, OV-IL15C plus CD8+ T cells or saline. Log-rank test was used to compare survival curves. **, P < 0.01.
