Figure 8.
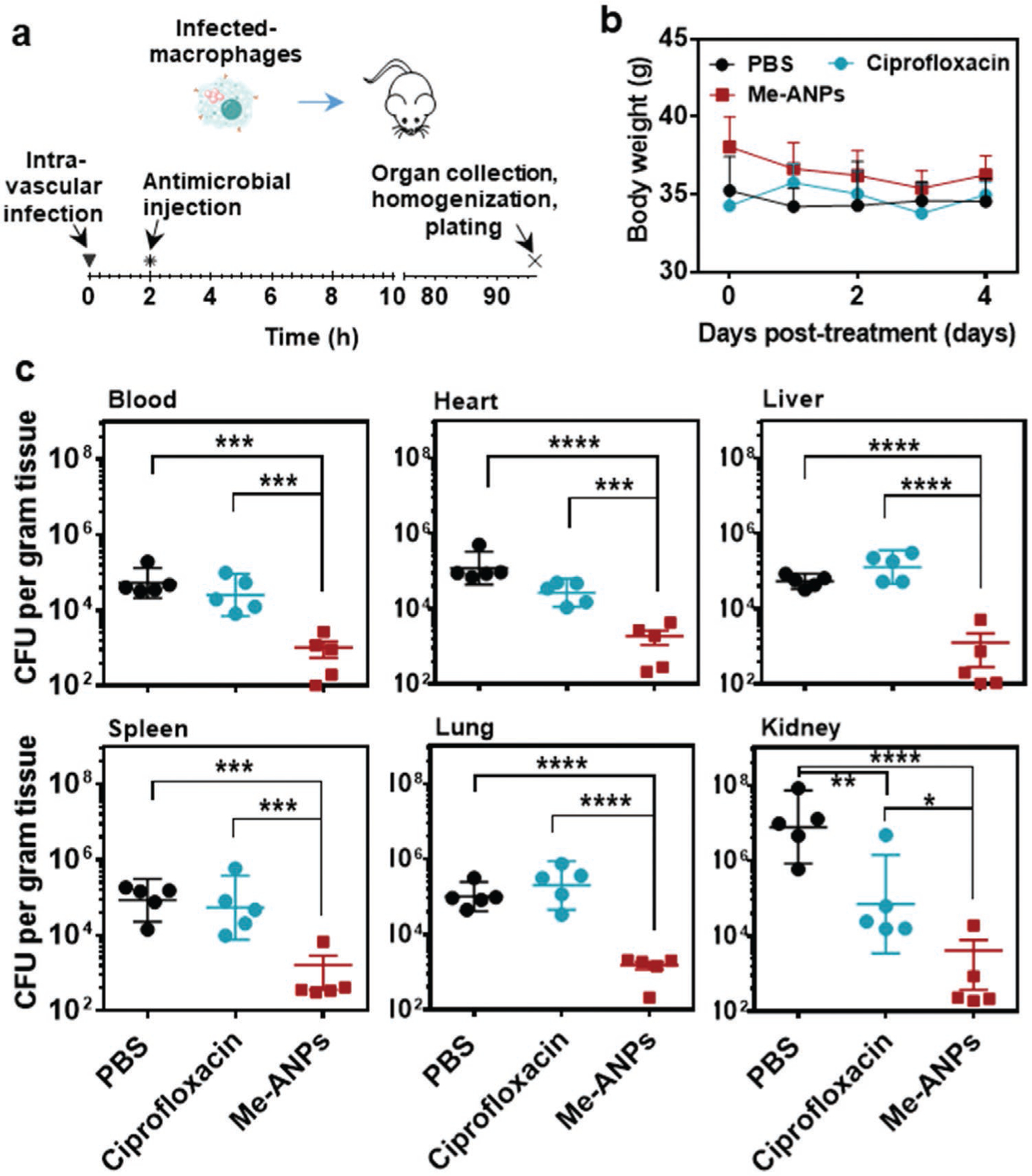
In vivo antimicrobial efficacy of mouse J774A.1 macrophage membrane-encapsulated, antimicrobial-conjugated nanoparticles, assessed in a mouse, intravenous organ infection model. a) Schematics of the mouse, intravenous infection model used. Organ infection was induced by intravenous injection of 200 μL of a suspension of mouse macrophages with intracellular S. aureus WHGFP, followed after 2 h by intravenous injection of 200 μL PBS, or PBS with ciprofloxacin or Me-ANPs. b) Body weight of the mice as a function of time posttreatment by intravenous injection. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations over 5 mice per group. c) The number of CFUs retrieved from 1 g of homogenized organ tissue for different organs, excised 4 days after intravenous antimicrobial injection. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations over 5 mice per group. Asterisks above the data points indicate statistical significance at p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***) and p < 0.0001 (****), one-way ANOVA test.
