Figure 2.
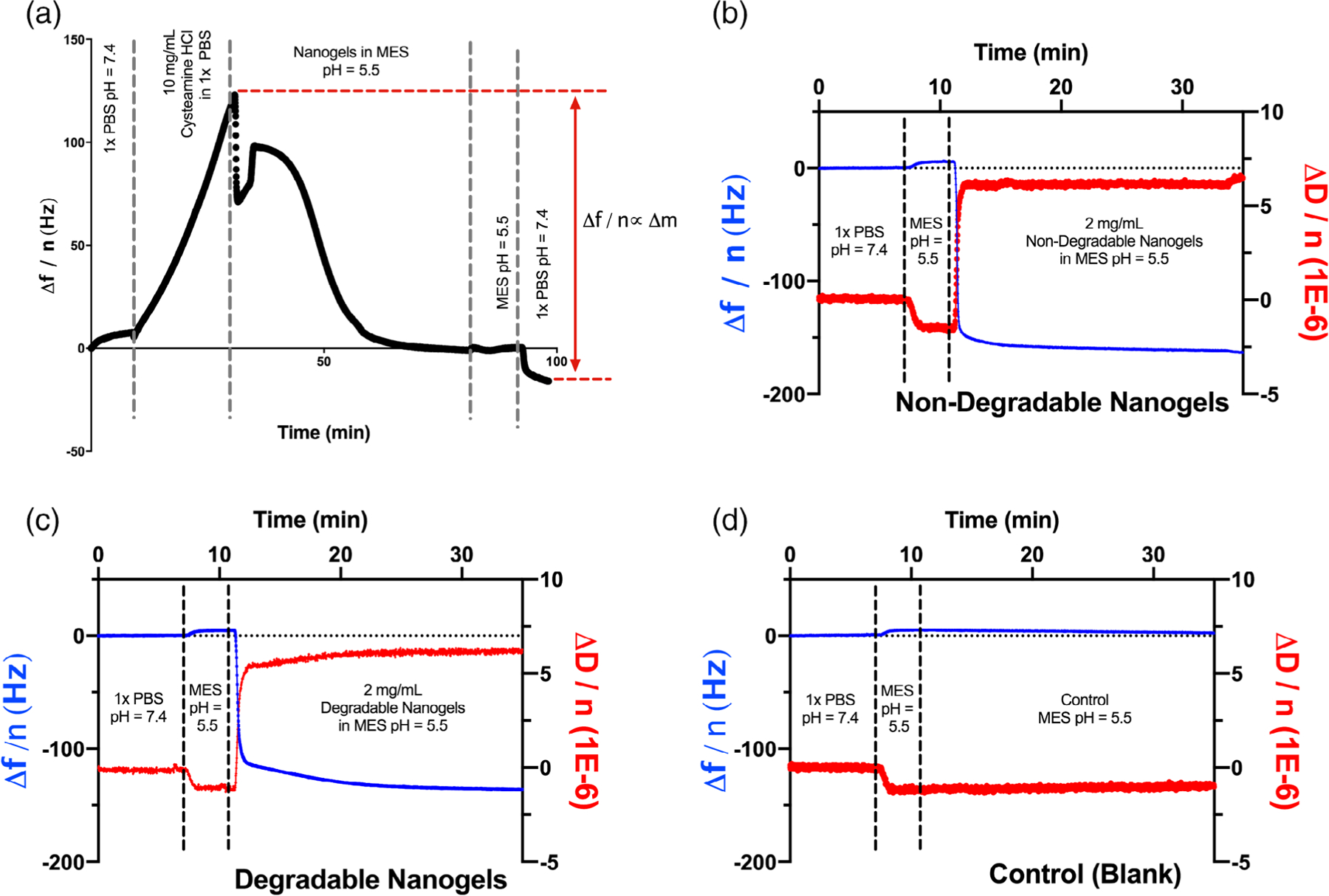
QCM-D sensor functionalization. (a) Cysteamine HCl forms a monolayer of free amines on the planar gold sensor through gold-thiol interactions. Nanogels were coupled to the amine monolayer via EDC-catalyzed crosslinking. The mass of nanogels coupled is linearly related to the reduction in resonance frequency during the coupling reaction. (b) Raw data for sensor functionalization with non-degradable poly(acrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) nanogels. Nanogel coupling increased the sensor bound mass by 3040 ng/cm2 as well as increased the viscosity of the sensor-associated layer. (c) A total of 2580 ng/cm2 degradable nanogels was conjugated to a parallel sensor. The viscosity of the sensor-associated layer increased in a manner similar to the non-degradable nanogels. (d) As expected, control sensors, without nanogels, exhibited no change in resonance frequency or dissipation.
