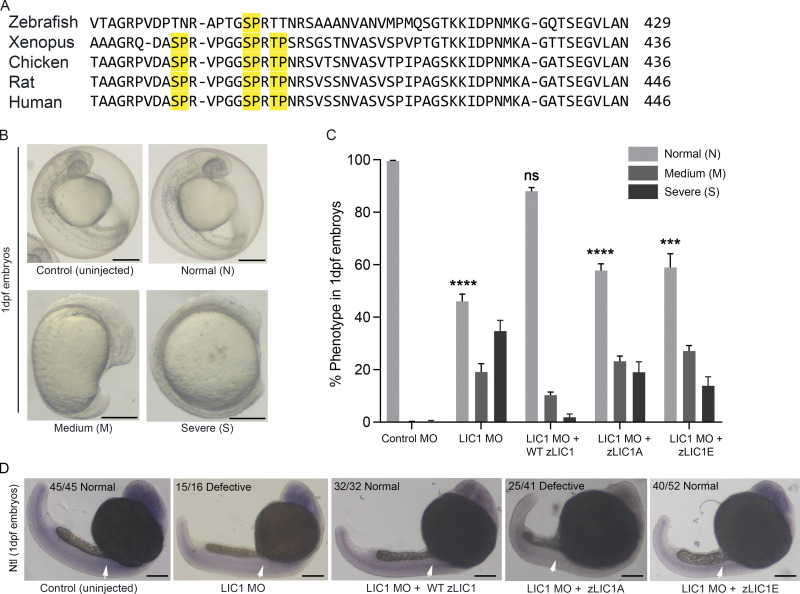
Figure 9.
LIC1-CTD phosphomutants are unable to efficiently rescue LIC1 depletion phenotypes in zebrafish embryos. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of representative vertebrate LIC1-CTDs. Yellow, conserved SP/TP cdk1 sites. (B) Bright-field images (5×) of 1-dpf zebrafish embryos. Representative control (uninjected) and zLIC1 MO–injected and/or rescued embryos showing three categories of phenotypes: normal (N), medium (M), or severe (S). (C) Fraction of embryos showing the phenotypes defined in E, upon rescue of zLIC1 depletion with the indicated zLIC1 mRNA constructs. P values calculated with regard to control MO. (D) Representative bright-field images of 1-dpf zebrafish embryos (5×), stained by ISH using a riboprobe against the zebrafish Ntl gene (purple). Numbers indicate the fraction of embryos showing the depicted phenotype. Arrows depict Ntl mRNA expression, which is weakened upon zLIC1 depletion or rescue with zLIC1A. Scale bar = 500 µm. Error bars = mean ± SEM. ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA).