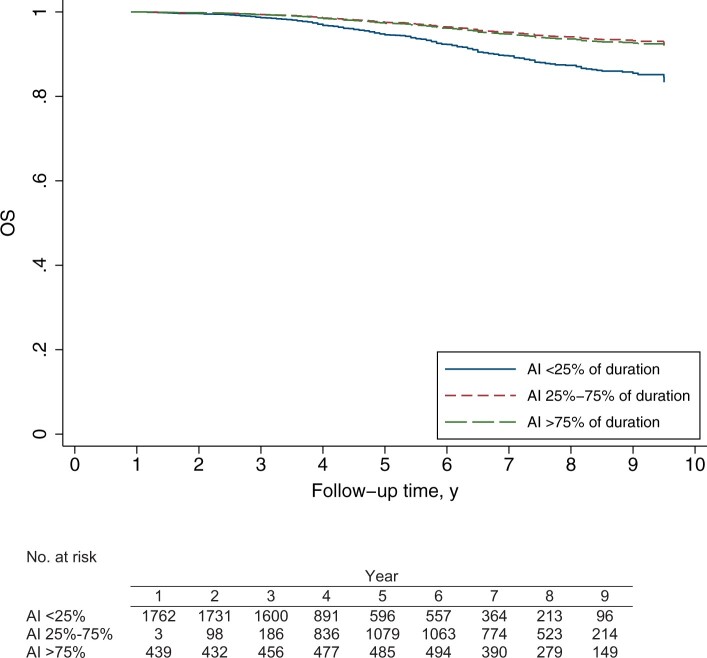
Figure 2.
Adjusted survival function of overall survival (OS) for 2284 estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer patients according to aromatase inhibitor (AI)–endocrine treatment ratio. Adjusted 5-year OS rates were 94.6% (95% CI = 93.6% to 96.1%) vs 97.6% (95% CI = 97.0% to 98.4%) vs 97.3% (95% CI = 96.4% to 98.4%) for AI less than 25%, 25%-75%, and AI greater than 75%, respectively. The AI–endocrine treatment ratio, included in the model as a time-dependent variable, is defined as the percentage of total endocrine treatment duration (AI+tamoxifen) spent on AI treatment. The survival functions are obtained from a Cox model at average values of age at diagnosis, trastuzumab use (included as a time-dependent variable), grade, number of positive lymph nodes, pathologic T-stage, progesterone receptor status, HER2 status, and ovarian ablation (included as a time-dependent variable).