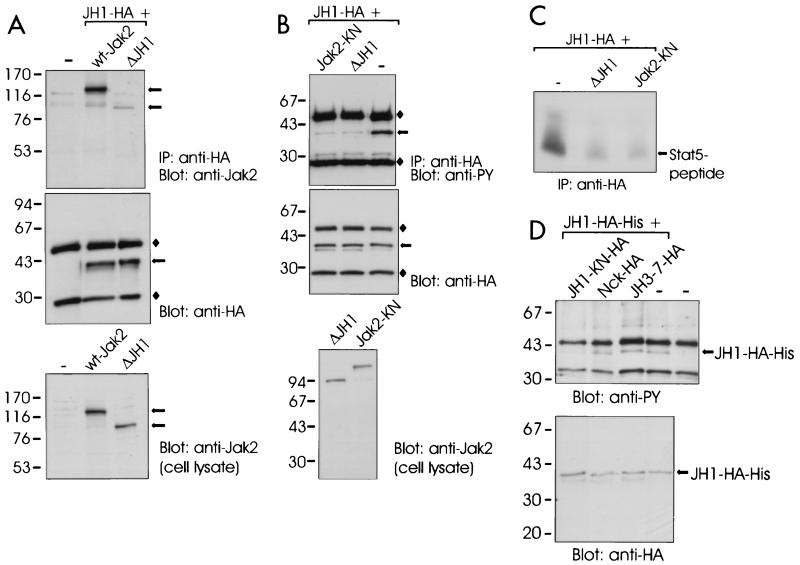
FIG. 6.
Effect of JH domains on activity of the Jak2 tyrosine kinase domain. (A) 293T cells were transfected with expression plasmids for JH1-HA and untagged wt-Jak2 or ΔJH1 or left untransfected (—). The cells were lysed in Brij 58 buffer, and the lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HA antibody. The immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS–4 to 15% PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-Jak2 or anti-HA antibodies. Aliquots of the cell lysates were analyzed by SDS–7.5% PAGE followed by anti-Jak2 immunoblotting. (B) 293T cells were transfected with JH1-HA expression plasmid alone (lane —) or together with expression plasmids for untagged ΔJH1 or Jak2-KN. JH1-HA was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HA antibody, analyzed by SDS–4 to 15% PAGE, and blotted with antiphosphotyrosine (anti-PY) or anti-HA antibodies. Aliquots of the cell lysates were analyzed by SDS–4 to 15% PAGE followed by anti-Jak2 immunoblotting. ⧫, Ig chains. (C) Aliquots of immunoprecipitates from panel 6B were subjected to in vitro kinase assays with Stat5-derived peptide and [γ-32P]ATP as substrates. The peptides were separated by SDS–20% PAGE followed by autoradiography. (D) 293T cells were transfected with an expression vector for HA- and histidine-tagged JH1 (JH1-HA-His) alone or together with expression plasmids for JH3-7-HA, JH1-KN-HA (K882E in JH1), or Nck-HA. JH1-HA-His was isolated by metal affinity, analyzed by SDS–4 to 15% PAGE, and blotted with antiphosphotyrosine (anti-PY) or anti-HA antibodies. The mobilities of the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown on the left in all panels. The arrows on the right indicate the mobilities of the Jak2 proteins.